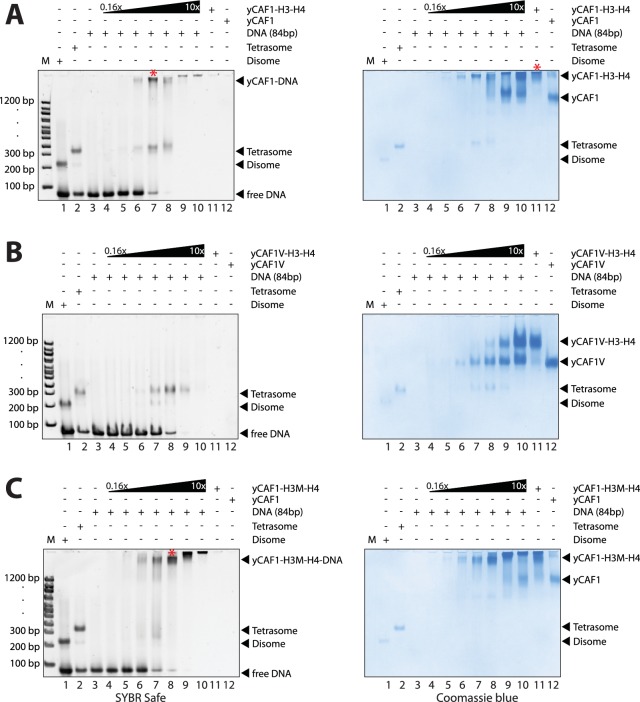
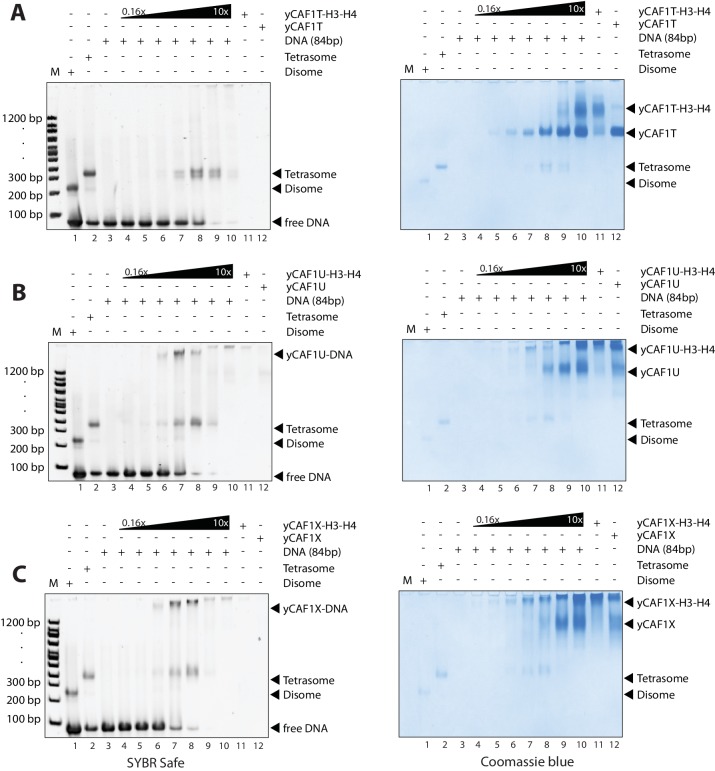
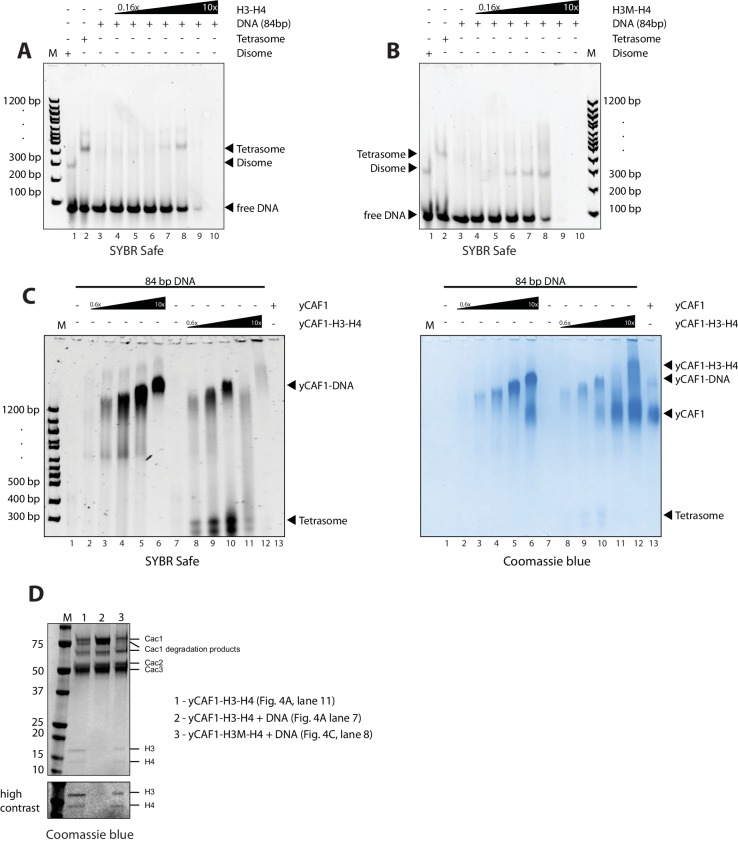
Figure 4. yCAF1 deposition of H3-H4.
(A) EMSA showing tetrasome deposition on 84 bp DNA. Increasing amounts of yCAF1-H3-H4 (0.15, 0.3, 0.61, 1.25, 2.5, 5 or 10 μM) were mixed with 1 μM 84 bp DNA and the bands resolved by native PAGE. Gels were stained for DNA with SYBR Safe (left panel) and for protein with Coomassie (right panel). (B) As above but for yCAF1V-H3-H4. (C) As above but for yCAF1-H3M-H4 (H3M contains the L126R/I130R mutation). * indicates extracted gel bands that we analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Figure 4—figure supplement 2D). All EMSA experiments were repeated at least two times with consistency.