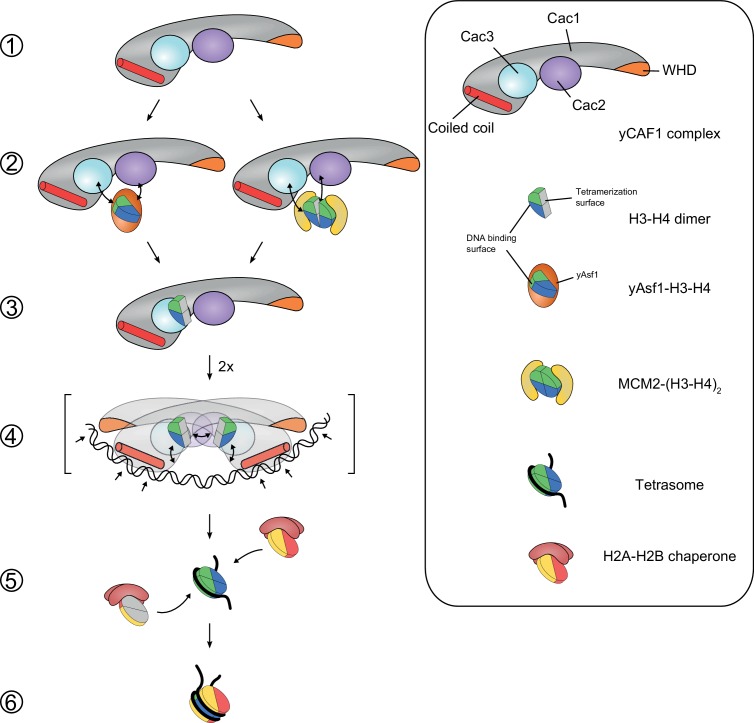
Figure 7. Model for yCAF1 recruitment and H3-H4 deposition.
Free monomeric yCAF1 (step 1) is loaded with dimeric H3-H4 through association of yAsf1 with the Cac2 subunit. Alternatively, loading can occur through hand over of H3-H4 from Mcm2 (step 2). yCAF1 binds the histones via their DNA binding and oligomerization surfaces (step 3). During DNA synthesis, two yCAF1-H3-H4 complexes bind cooperatively to an extended DNA element >50 bp (step 4) to deposit H3-H4 dimers and form tetrasomes. The WHD (orange) and coiled-coil (red) DNA-binding domains of yCAF1 are required for deposition of H3-H4 tetramers. The requirement of an extended free DNA region together with PCNA interaction may direct yCAF1 activity to replication forks. H2A-H2B chaperones like NAP1 or FACT recognize the tetrasome intermediate and deposit two copies of H2A-H2B (step 5) to form a complete nucleosome (step 6).