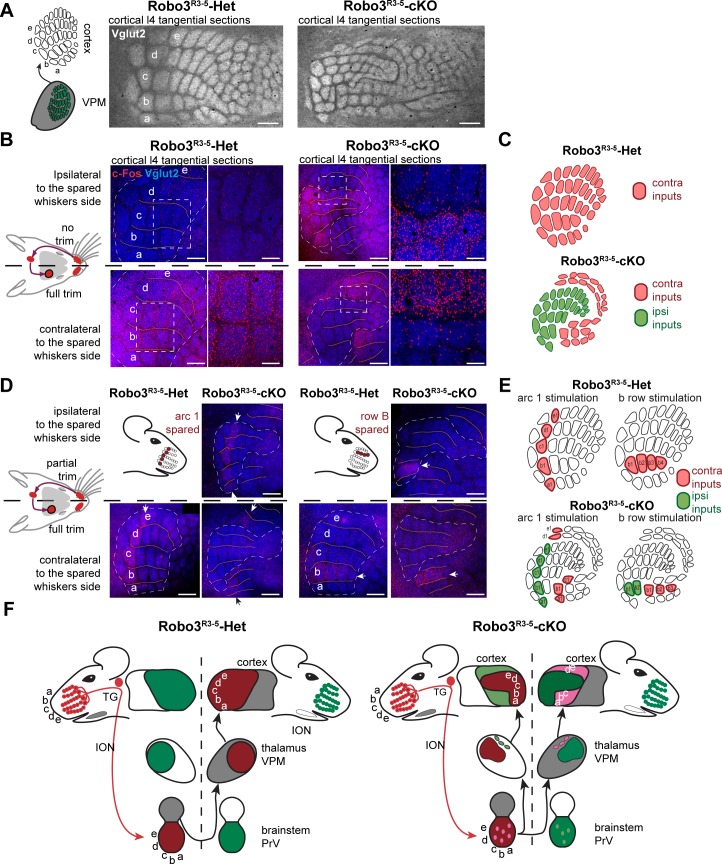
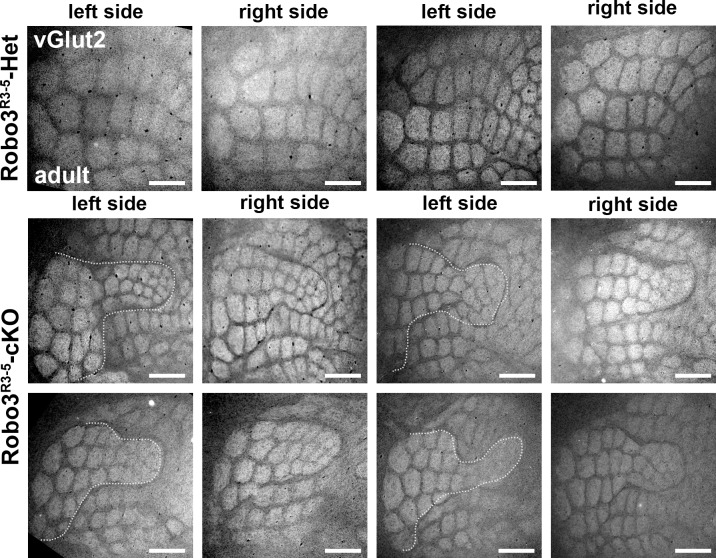
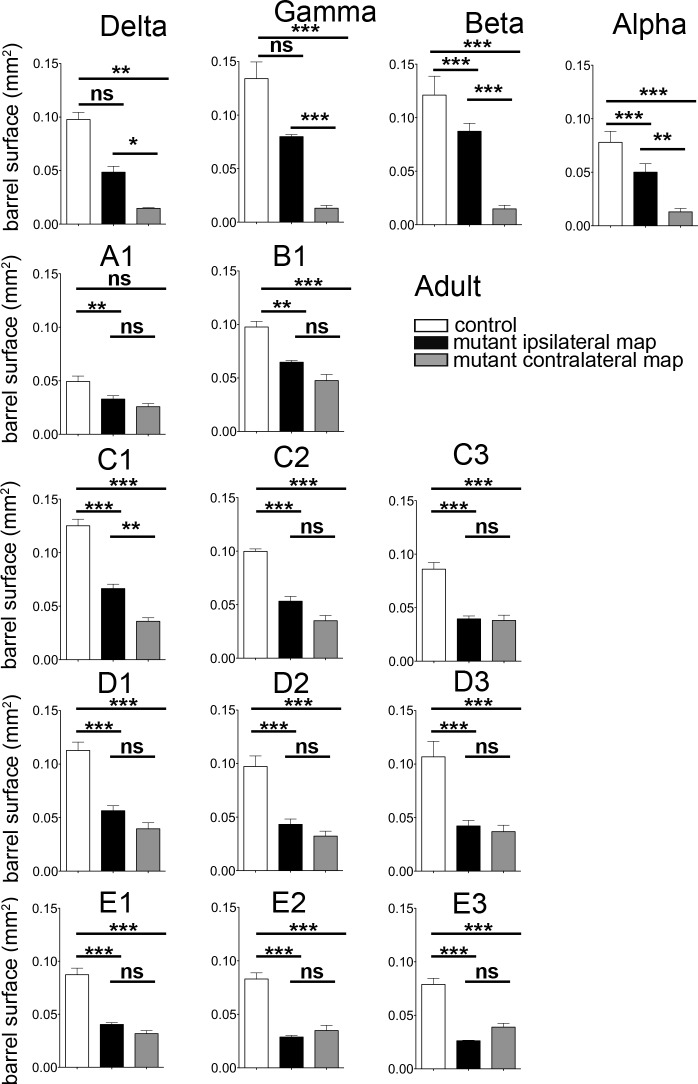
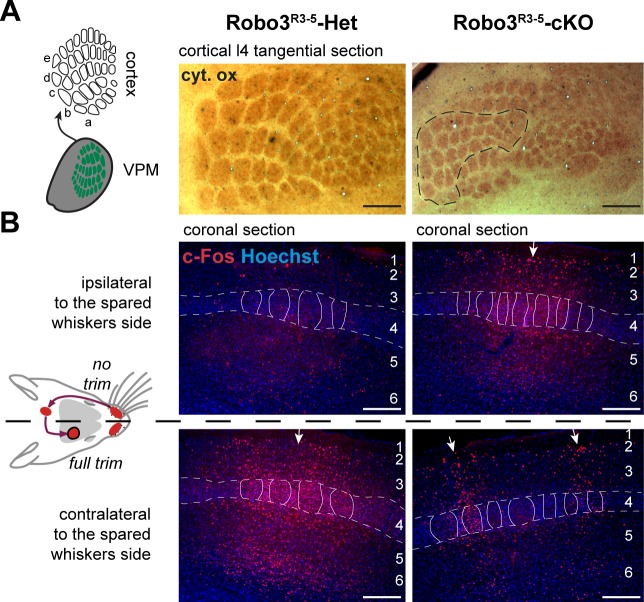
Figure 5. Bilateral inputs to the barrel cortex in Robo3R3-5-cKO mice.
(A) Tangential sections through the barrel cortex from P10 mice stained for anti-Vglut2. Barrels are more numerous and smaller in mutants. (B) Tangential sections through Flat-mounted cortices at the level of the barrel cortex in whisker-deprived adult mice immunostained for Vglut2 and c-Fos. In controls, c-Fos+ cell density is high in the barrel cortex contralateral to the intact whiskers and low on the ipsilateral side. In Robo3R3-5-cKO mutants, c-Fos expression is induced bilaterally in complementary domains on either side of the cortex, ipsilateral and contralateral to the stimulated side. (C) Interpretation of the results from (B). (D) Tangential sections through Flat-mounted cortices at the level of the barrel cortex, in whisker-deprived adult mice immunostained for Vglut2 and c-Fos. The left side of the face was fully shaved, while only the first arc (left panels) or b row (right panels) was spared on the right side. Only the contralateral sides are shown for controls. Mutants show bilateral patterns of c-Fos (E) Schematic representation of the whisker map deduced from c-Fos activation patterns. (F) General model for the wiring of the Robo3R3-5-cKO mutant mice. Scale bars are 200 µm.