Figure 8. Restraint stress and C1 neuron stimulation produce opposite effects on arterial pressure and heart rate.
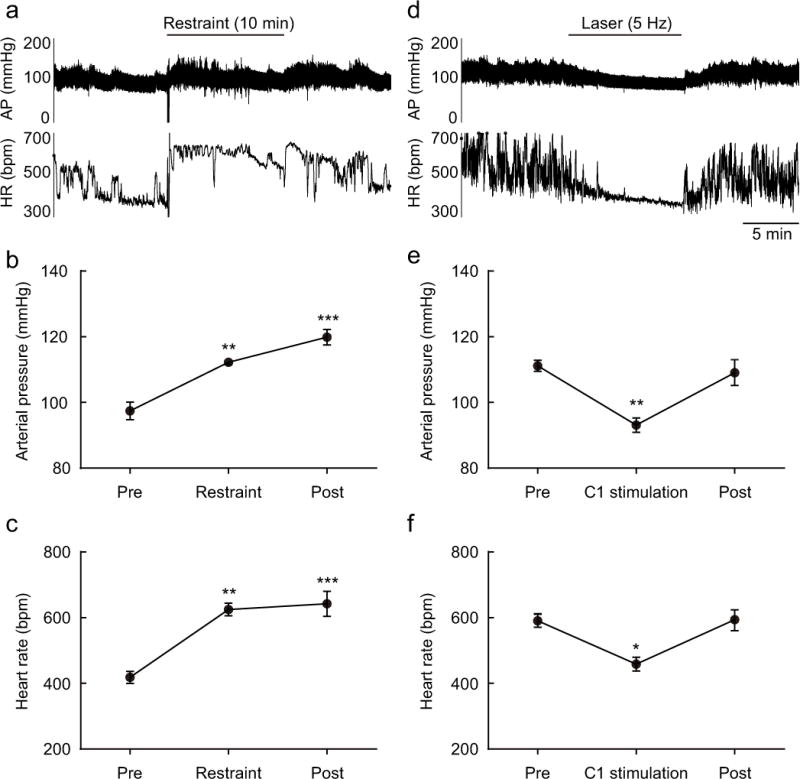
(a) Effect of restraint stress on arterial pressure (AP) and heart rate (HR) in a DBH-cre mouse. (b and c) Mean AP and HR before (Pre), during and after (Post) restraint (each period: 10 min) in DBH-cre mice (n = 4). Statistics: one-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer test; [F(2, 9) = 29.11, P = 0.0001] (b) and [F(2, 9) = 21.93, P = 0.0003] (c). * vs. Pre. Double symbols, P < 0.01 and triple symbols, P < 0.001. (d) Effect of C1 stimulation (10 ms, 5 Hz, 10 min) on arterial pressure (AP) and heart rate (HR) in a DBH-cre mouse. (e and f) Effect of C1 neuron stimulation (laser 5 Hz) on AP and HR in DBH-cre mice. Mean AP and HR before (Pre), during and after (Post) C1 neuron stimulation (each period: 10 min) (n = 4/group). Statistics: one-way repeated measure ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer test; [F(2, 9) = 12.7, P = 0.0024] (e) and [F(2, 9) = 9.249, P = 0.0066] (f). * vs. Pre. Single symbols, P < 0.05 and double symbols, P < 0.01.
