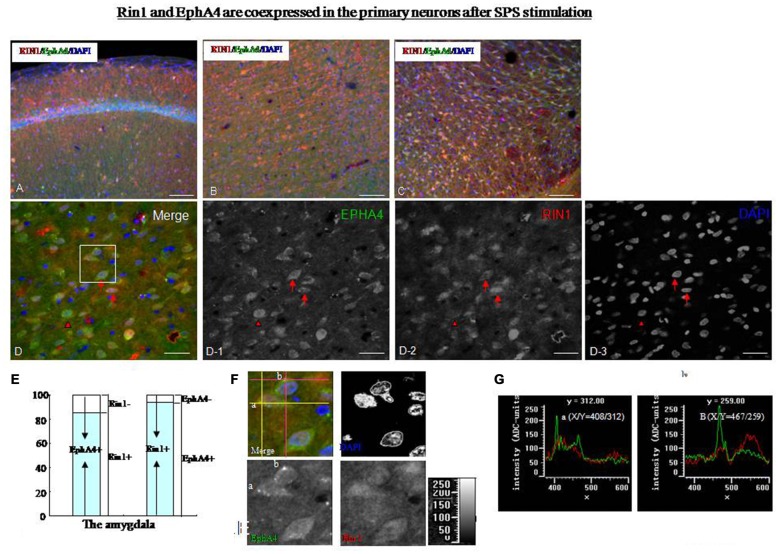
Figure 7.
(A–C) Dual-immunofluorescence images showing that Rin1-ir and EphA4-ir were colocalized in the hippocampus (A), cingulate cortex (B), and thalamus (C) of SPS rats. (D) Higher magnification image of the amygdala shows colocalization of Rin1/EphA4 (arrow) and EphA4- or Rin1- positive cells (arrowhead). EPHA4: D-1; RIN1: D-2; DAPI: D-3. (E) Statistical analysis indicated that about 88% of EphA4-positive cells were Rin1-positive, and 93% of Rin1-positive cells were EphA4-positive in the amygdala. (F) Higher magnification images of the area in the white box in panel (D). Some bright clusters were detected (merge). Two clusters (a and b) were selected by positioning the coordinates (a: intersection of two yellow lines; b: intersection of two pink lines). (G) Intensity of points a and b. The green line shows the intensity of EphA4, and the red line shows the intensity of Rin1. EphA4 was expressed at peak intensity at points a (X/Y = 408/312) and b (X/Y = 467/259; *P < 0.05 vs. the control group; Bar in A–C: 100 μm; Bar in D: 20 μm).