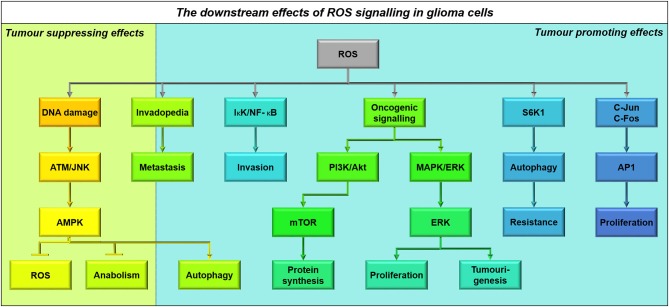
Figure 12.
The downstream effects of ROS signaling in glioma cells. Activation of AMPK as a result of oxidative damage induced by ROS, has both tumor suppressive and promotive effects within glioma cells, through AMPK signaling (Alexander and Walker, 2011). Additionally ROS aids in oncogenic signaling resulting in the activation of pathways involved in metastasis, invasion, proliferation, and resistance (Boonstra and Post, 2004). ROS mediates the formation of invadopedia involved in metastasis and inflammatory signaling through NF-kB to promote matrix degradation and invasion (Zhang et al., 2015). Additionally PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways are also augmented resulting in increased proliferation, as well as increasing c-Jun and c-Fos formation of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factor involved in proliferation (Benhar et al., 2002; Waris and Ahsan, 2006). Finally, ROS are also involved in S6K1 activation which acts to induce autophagy providing chemotherapeutic resistance (Sarbassov and Sabatini, 2005).