Figure 14.
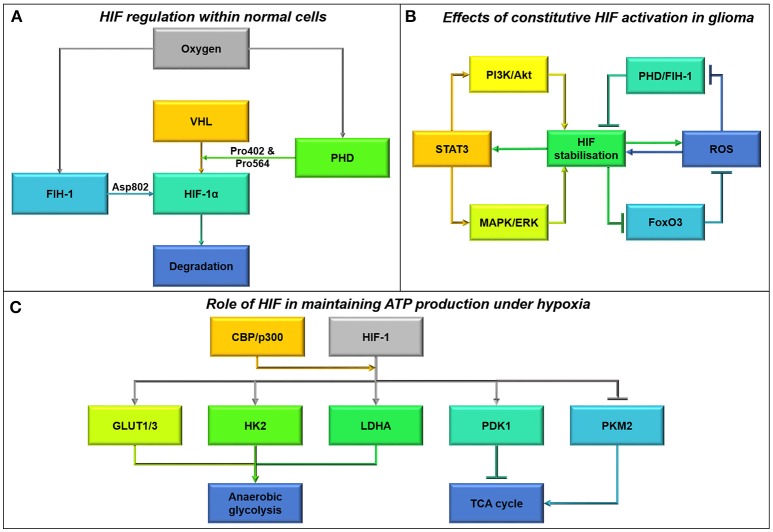
(A) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) regulation within normal cells. There are two main avenues governing HIF-1α within normal cells, involving the factor-inhibiting hypoxia-1 (FIH-1) and Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) proteins (Semenza, 2010). The activity of these proteins is regulated by oxygen levels, whereby FIH-1 hydroxylates HIF-1α at Asp802 blocking its transcriptional activity, whereas VHL activity is reliant on prolyl-hydroxylase (PHD) to hydroxylate Pro402 and everPro564 under oxygenated conditions, marking HIF for degradation by VHL (Semenza, 2010). However, when oxygen levels are low HIF is not marked for degradation and is therefore its transcriptional activity is unrestrained. (B) Effects of constitutive HIF activation in glioma. The constitutive activation of HIF under normal oxygen tension is known as pseudo-hypoxia. Oncogenic signaling in cancer cells acts to stabilize HIF under normoxia primarily through the activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways (Qiang et al., 2012; Mimeault and Batra, 2013). In turn, as a result of HIF transcription STAT3 is upregulated resulting in further activation of these oncogenic pathways (Mimeault and Batra, 2013; Qiang et al., 2012). HIF stabilization often arises in concert with ROS production, which acts to stabilize HIFs by oxidizing the catalytic iron center of PHD and FIH-1, limiting HIF degradation (Chandel et al., 2000; Semenza, 2010). Reduced FoxO3 activity as a result of oncogenic signaling and HIF transcription also acts to increase ROS production as part of a feed-forward mechanism (Ferber et al., 2012). (C) Role of HIF in maintaining ATP production under hypoxia. Upon stabilization the HIF-1 complex acts in concert with the CREB-binding protein (CBP)/p300 co-activator to alter the transcription of multiple genes involved in metabolism (Semenza, 2010). Through increasing the transcription of GLUT1/3, HK2, PDK1, and LDHA, HIF-1 increases glucose uptake and glycolysis whilst inhibiting the Kreb's cycle and oxidative metabolism (Semenza, 2010; Kucharzewska et al., 2015). Additionally, HIF-1 transcription also inhibits PKM2 activity to limiting flux through the Kreb's cycle and oxidative metabolism (Kim et al., 2015).