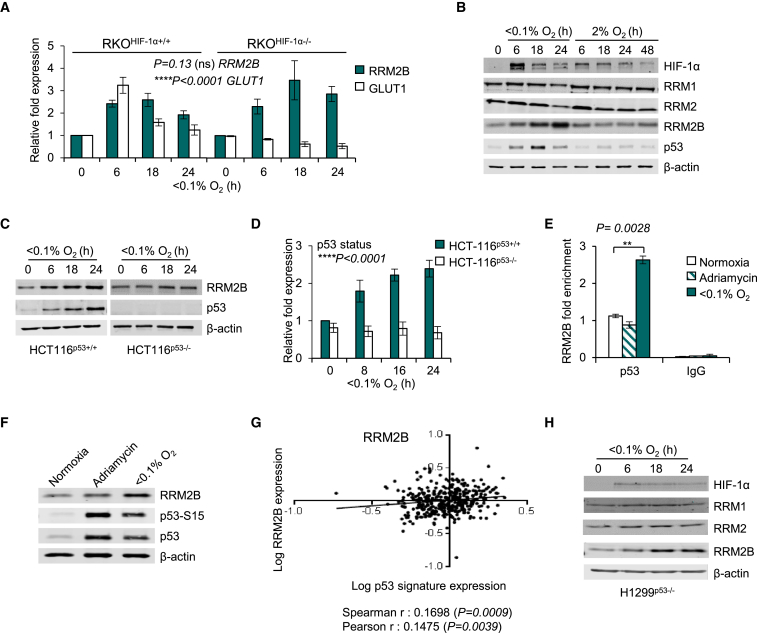
Figure 2.
RRM2B Is Induced in Hypoxia
(A) mRNA levels of RRM2B and GLUT1 in RKOHIF-1α+/+ and RKOHIF-1α−/− cells in <0.1% O2 assayed by qPCR and normalized to 18S.
(B) Immunoblots of RKO cells exposed to 2% and <0.1% O2 for the times indicated. p53 and RRM2B protein induction are observed only in <0.1%O2.
(C and D) Immunoblots (C) and RRM2B mRNA levels (D) of HCT116p53+/+ and HCT116p53−/− exposed to <0.1% O2 for the times indicated.
(E) qPCR for p53 ChIP in RKO cells treated with Adriamycin (2 μM, 6 hr) or exposed to either normoxia or <0.1% O2 (6 hr).
(F) Immunoblots of RKO cells treated as in (E).
(G) Expression of RRM2B (log10 conversion) in the colorectal adenocarcinoma TCGA datasets is shown against hypoxia dependent p53-inducible group of genes (log10 conversion).
(H) Immunoblots of RNR subunits in H1299p53−/− (non-small cell lung carcinoma) cells exposed to <0.1% O2 for the times indicated.
For all panels (except G), n = 3 (biological replicates); data in (A) and (D) represent mean ± SEM; and (E) shows representative mean of technical triplicates ± RQmax/RQmin. HIF-1α status and p53 status was examined by two-way ANOVA analysis; two-tailed Student’s t test was applied in (E); (ns) indicates a non-significant change. See also Figure S2.