Figure 2.
apc14Δ and apc15Δ Mutants Both Perturb the Interaction between MCC Complexes and the APC/C, but in Opposite Ways
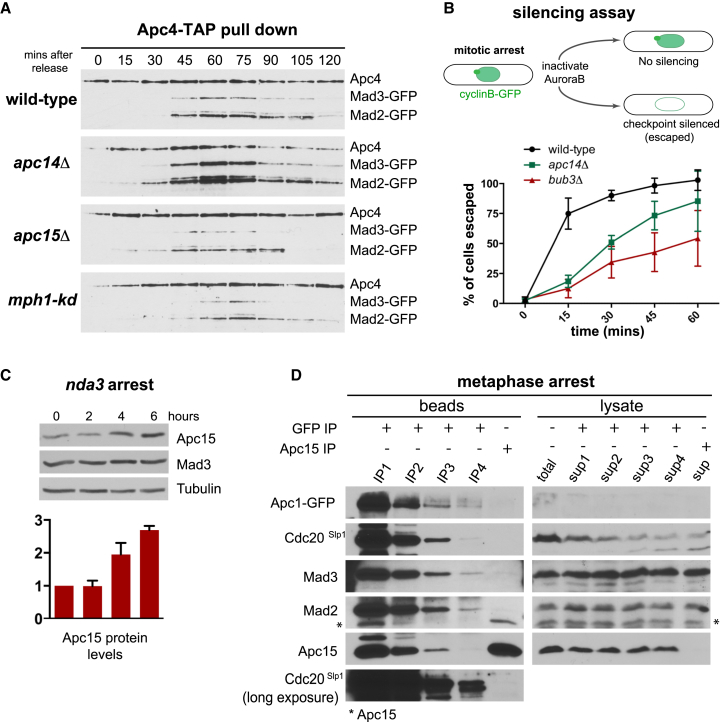
(A) APC/C binding time courses. cdc25-22 apc4-TAP mad3-GFP cultures were synchronized at G2/M by cdc25 block and release, cell samples were taken at 15-min intervals, and Apc4-TAP was pulled down and analyzed for associated checkpoint proteins (Mad3 and Mad2). The cells from each time point were fixed in methanol and the number of binucleate cells was determined by DAPI staining DNA. This experiment was repeated twice, and a representative example is shown here.
(B) Checkpoint silencing assay. nda3KM-311 cdc13-GFP strains were arrested by shifting to 18°C to de-polymerize microtubules and thereby activate the spindle checkpoint. The Ark1-as kinase was then inhibited with 5 μM 1NM-PP1 and live-cell samples were analyzed at 15-min intervals. Ark1 inhibition activates the APC, and Cdc13-GFP is rapidly degraded in wild-type cells. The mitotic index was scored in live cells by analyzing the levels and localization of Cdc13-GFP (cyclin B). In arrested cells, this is nuclear with a bright signal at the spindle pole bodies (SPBs). The number of cells that degrade Cdc13-GFP is shown as a percentage of arrested cells at t = 0. This experiment was repeated at least three times (with at least 100 cells scored per strain at each time point), and the data are plotted as the mean ± SD.
(C) nda3-KM311 mutants were grown to log phase and then shifted to 18°C for 6 hr, taking time points at 2-hr intervals. Whole-cell immunoblots were then analyzed for levels of Apc15 Mad3 and tubulin. This experiment was repeated three times, and the data are plotted as the mean ± SD. See Figure S2B for quantitation of Apc15 levels through the cell cycle.
(D) Cells were arrested in metaphase, through nda3 arrest, and lysates were prepared and then immunodepleted for APC/C complexes through four rounds of Apc1-GFP immunoprecipitation. Apc15 was then immunoprecipitated from the final supernatant. The five sets of beads were then analyzed for associated Cdc20 and checkpoint proteins, revealing high levels of free Apc15 after APC/C depletion. This experiment was repeated twice.
See also Figure S2.