Figure 4.
A Free Pool of Cdc20M-Mad3-Mad2-Cdc20A Accumulates in apc15Δ Mutants
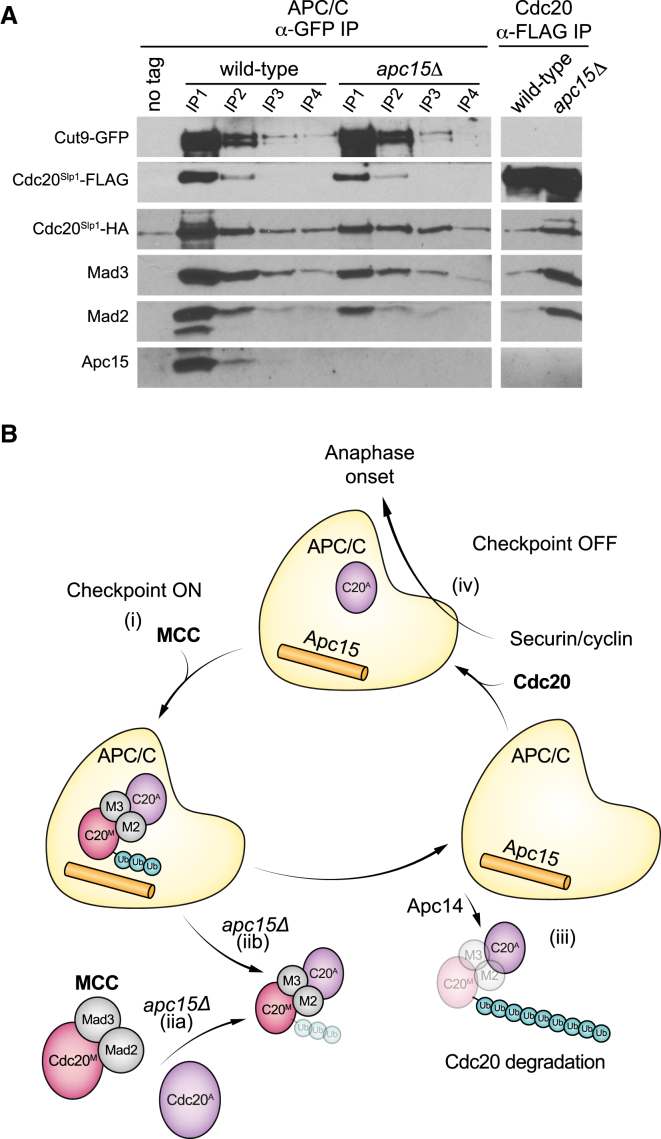
(A) The MCC (Cdc20M-Mad3-Mad2)-Cdc20A complex can be found in the APC/C-depleted supernatant, and the complex accumulates in apc15Δ. Mitotic lysates were prepared from cdc25-22 cdc20-HA cdc20-FLAG Apc6Cut9-GFP (60 min after cdc25 block and release) and then immunodepleted for APC/C complexes through four rounds of cut9apc6-GFP immunodepletion. Cdc20-FLAG was then immunoprecipitated from the resulting supernatant and immunoblotted to look for associated Cdc20-HA and checkpoint proteins. The MCC (Cdc20M-Mad3-Mad2)-Cdc20A is immunoprecipitated without Apc6Cut9-GFP or Apc15. This experiment was repeated twice.
(B) Models of MCC binding and Cdc20 ubiquitination, in wild-type cells and apc15 mutants. (i) When the checkpoint is on, the MCC binds to Cdc20-APC/C and in fission yeast this interaction is stabilized by Apc15. The C terminus of Mad3 (KEN2 and associated ABBA motifs) is critical for this stable interaction with the second molecule of Cdc20 (Cdc20A). (iia) In apc15Δ cells, the MCC could preferentially bind free Cdc20A. (iib) In the absence of Apc15, the MCC complex is weakly bound and Cdc20M is inefficiently ubiquitinated. It is released with short ubiquitin chains in the form of Cdc20M-Mad3-Mad2-Cdc20A. Note that both molecules of Cdc20 are released from the APC/C. (iii) In wild-type cells Cdc20M is efficiently poly-ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation. Apc14 function is required for efficient release of the MCC. (iv) The checkpoint is off; APC/C is now free to be bound by the Cdc20A activator, which can catalyze the poly-ubiquitination of securin and cyclin, leading to anaphase onset.
See also Figure S4.