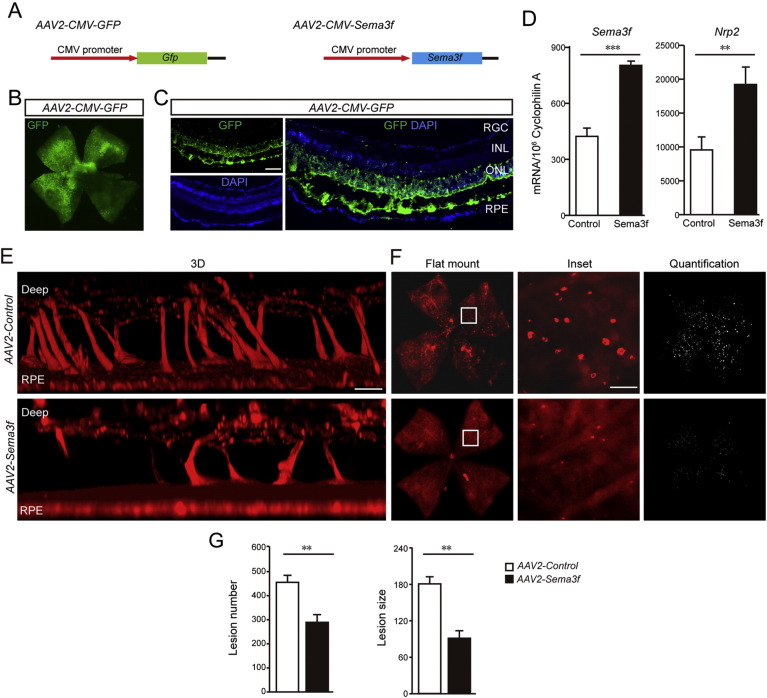
Fig. 2.
AAV2-CMV-Sema3f suppresses subretinal neovascularization induced by Vldlr deficiency.
(A) AAV2 constructs carrying Sema3f or GFP driven by CMV promoter. (B) Representative retinal flatmount image of a C57Bl6/J wild type animal showing that over 70% of the retina is successfully transfected by AAV2-CMV-GFP delivered by a single subretinal injection. (C) Representative cross section from a C57Bl6/J wild type treated by a single subretinal injection with AAV2-CMV-GFP showing efficient transfection. Green: GFP; blue: nuclear DAPI. Note that the dark band between ONL and RPE is due to artificial tissue separation during preparation. (D) Increased mRNA level of Sema3f is confirmed in AAV2-CMV-Sema3f- infected retinas compared with AAV2-CMV-Vector-infected retinas (n = 6). The mRNA level of Nrp2 was induced in AAV2-CMV-Sema3f- infected retinas compared with AAV2-CMV-Vector-infected retinas (n = 6). (E–G) 3D reconstruction, representative images of flat-mounts and quantification of neovascular lesion number and size showing that AAV2-CMV-Sema3f suppresses subretinal pathological neovascularization in Vldlr−/− retinas at P16. Lesions on flat mount were highlighted (white) in F (right panel) and enlarged in inset. Scale bar, 500 μm for flatmount, 250 μm for inset, 1000 μm in 3B; 100 μm in 3C and D.