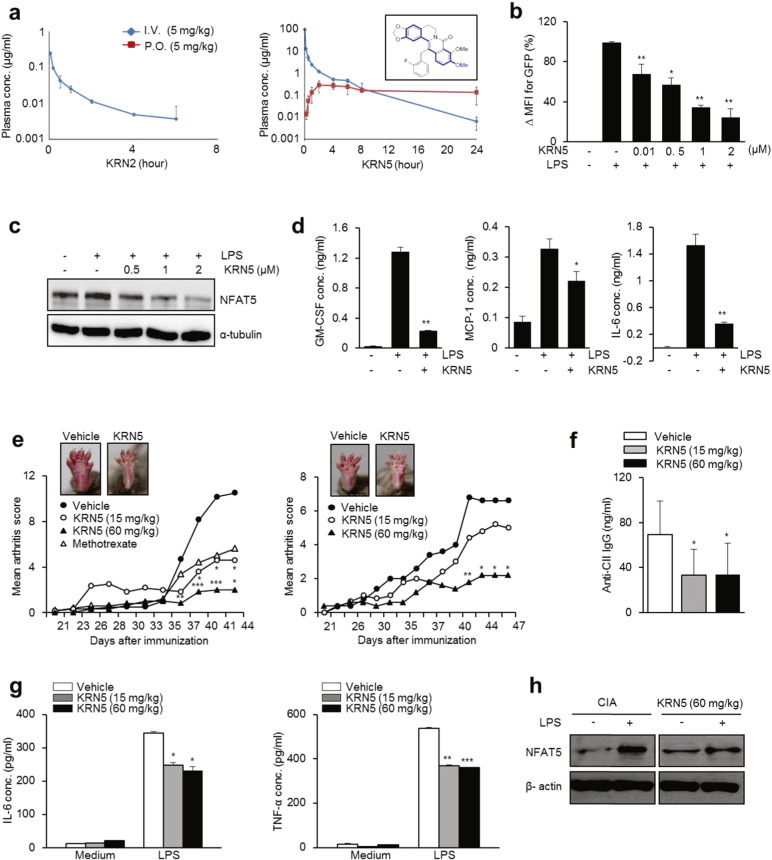
Fig. 6.
Pharmacokinetic profiles of KRN5, an oxo derivative of KRN2, and its effects as an anti-NFAT5 drug candidate. (a) Comparison of pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles of KRN2 (left) and KRN5 (right) in rat according to Intravenous (I.V.) or Per os (P.O.) administration. Figure in the box shows the structure of KRN5 (right panel). (b) KRN5 was dose-dependently added to RAW 264.7 cells transfected with NFAT5-GFP reporter system for 1 h. GFP expression was measured by flow cytometry. Values are the mean ± SD for % ΔMFI. *P < 0.005, **P < 0.001. (c) RAW 264.7 cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h in the presence of KRN5 as indicated doses. NFAT5 protein was detected by western blot analysis. (d) RAW 264.7 cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h in the presence of KRN5 (1 μM). Level of cytokines (GM-CSF, MCP-1, and IL-6) in the culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. (e) Disease severity of CIA-induced mice (n = 5, respectively) orally administrated with KRN5 (15 and 60 mg/kg) or vehicle for 44 and 47 days. Methotrexate (15 mg/kg) was used as a positive control. Values are the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005 versus mice group with vehicle. Each graph shows two independent experiments. (f) Sera from CIA-induced mice injected with KRN5 or vehicle were collected on day 44. Anti-bovine CII IgG level was measured by ELISA. Values are the mean ± SD. *P < 0.005 versus mice group with vehicle. (g–h) Mouse splenocytes isolated from CIA-induced mice treated with vehicle or KRN5 (15 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg) were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h and then the culture supernatants were harvested. (g) IL-6 and TNF-α level in the supernatant were measured by ELISA. Data show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005 and ***P < 0.001 versus unstimulated cells. (h) NFAT5 protein level was determined by western blot analysis. Data are the representative of three independent experiments with similar results.