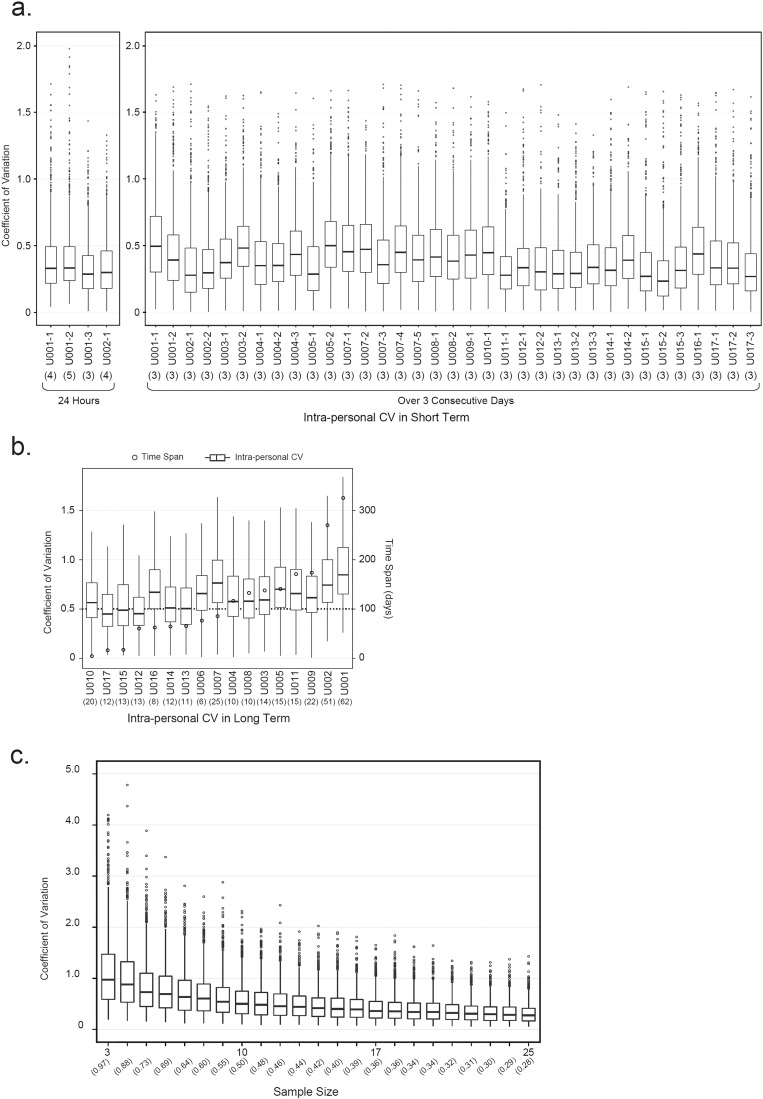
Fig. 2.
The effects of sampling time span and sample size on intra-personal variations of the urine proteome. (a) Intra-personal variations of urine proteomes in short term (24 h and 3 consecutive days) of urine sampling. Coefficients of variation (CVs) were calculated from proteins quantified in all samples in each dataset. Number in parenthesis under X-axis represented sample number in each dataset. For variations within 24 h (median CVs 0.29–0.33), 4 datasets were acquired from two individuals (U001 and U002); For variations over 3 consecutive days (median CVs 0.23–0.5), 35 datasets were acquired from 16 donors (U001–U005 and U007–U017). (b) Intra-personal variations of human urine proteomes in long term (> 60 days) of urine sampling. Number in parenthesis under X-axis represented sample number in each dataset. Of 17 donors in BCM dataset, intra-personal CVs for long term (> 60 days) could be calculated from 14 donors (U001–U009, U011–U014, and U016). For convenience of comparison, intra-personal CVs from U010, U015, and U017 (time span for urine sampling are 5, 17, and 18 days, respectively) were also plotted in the same graph (the first 3 boxes). Median CVs for 17 donors range from 0.45–0.87. (c) The effect of sample size on intra-personal variation of human urine proteome. The graph was plotted according to the dataset of U001. Number in parenthesis under X-axis represented median CV in each dataset. CVs in Y-axis were calculated with 100 iterations of mean iFOT5 for each protein in each subset size.