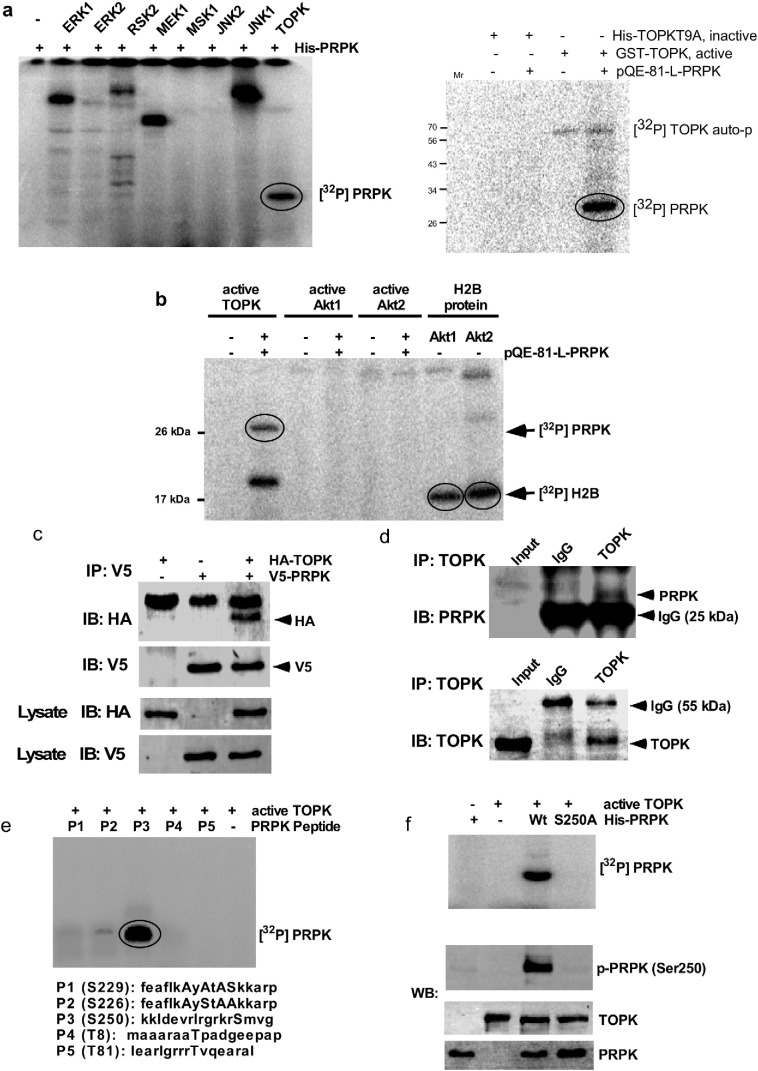
Fig. 1.
TOPK binds with and phosphorylates PRPK at Ser250 in vitro. (a) The pQE-81L-PRPK (His) fusion protein was used as a substrate for an in vitro kinase assay with active protein kinases as shown (left panel) and for His-TOPKT9A fusion protein as inactive compare with TOPK, active (right panel). (b) Phosphorylation of PRPK by TOPK or Akt1/2 was compared using in vitro kinase assays and histone H2B was used as positive control for Akt1/2. (c) TOPK binds with PRPK in HEK293 cells after transient transfection. The pcDNA3-HA-TOPK and pcDNA3-V5-PRPK plasmids were co-transfected into HEK 293 cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 and then probed with anti-HA. (d) TOPK binds with PRPK in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Endogenous TOPK was immunoprecipitated from HCT116 cells and then probed with anti-PRPK. (e) Five PRPK peptides were designed for an in vitro kinase assay with active TOPK. (f) For in vitro kinase assays, a wildtype His-PRPK (Wt) or His-PRPK-S250A mutant (S250A) protein was used as a substrate for active TOPK. For (a), (b), (e) or (f, upper panel), reactive products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Reactive products for (f, lower panel) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Western blot with specific antibodies.