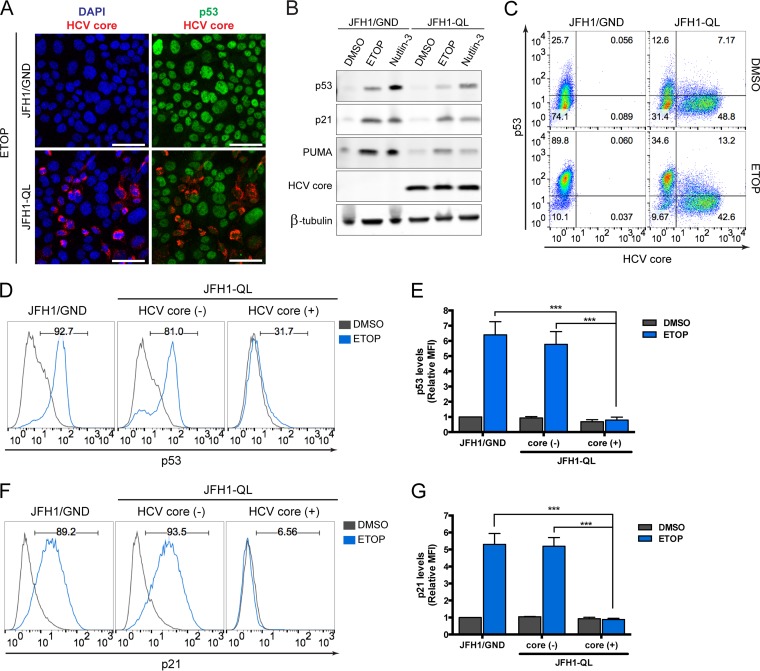
FIG 2 .
HCV replication inhibits p53 activation following DNA damage. (A) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy for p53 and HCV core protein in HepG2/miR-122 cells electroporated with genome-length HCV RNA (JFH1-QL) or a nonreplicating control RNA (JFH1/GND) and treated 72 h later with 100 μM etoposide (ETOP) or DMSO for 2 h. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI. Bars, 50 μm. (B) Immunoblots of p53, p21, PUMA, and HCV core protein in HepG2/miR-122 cells electroporated with JFH1-QL or JFH1/GND RNA and treated 72 h later with 50 μM ETOP, 10 μM MDM2 inhibitor (nutlin-3), or DMSO for 6 h. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of p53 and HCV core protein levels in cells treated as described for panel A. Quadrants are based on staining with isotype control antibodies. The frequency of events in each quadrant is represented as the percentage of total gated events. (D) p53 accumulation in cell populations from panel C that do not express HCV core [HCV core (-)] versus cell populations that express HCV core [HCV core (+)]. The numbers indicate the percentages of p53-positive cells following etoposide treatment. (E) Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) values for p53 for the indicated populations are shown normalized to JFH1/GND-electroporated, DMSO-treated controls. Relative MFI values represent the means plus standard errors of the means (SEM) (error bars) from three independent experiments. (F) p21 upregulation in HCV core (-) versus HCV core (+) cells treated with 50 μM ETOP or DMSO for 6 h. The numbers indicate the percentages of p21-positive cells following etoposide treatment. (G) MFI values for p21 are shown normalized to JFH1/GND-electroporated, DMSO-treated controls. Relative MFI values represent the means plus SEM from three independent experiments. Values that are significantly different (P < 0.0001), by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons are indicated by a bar and three asterisks.