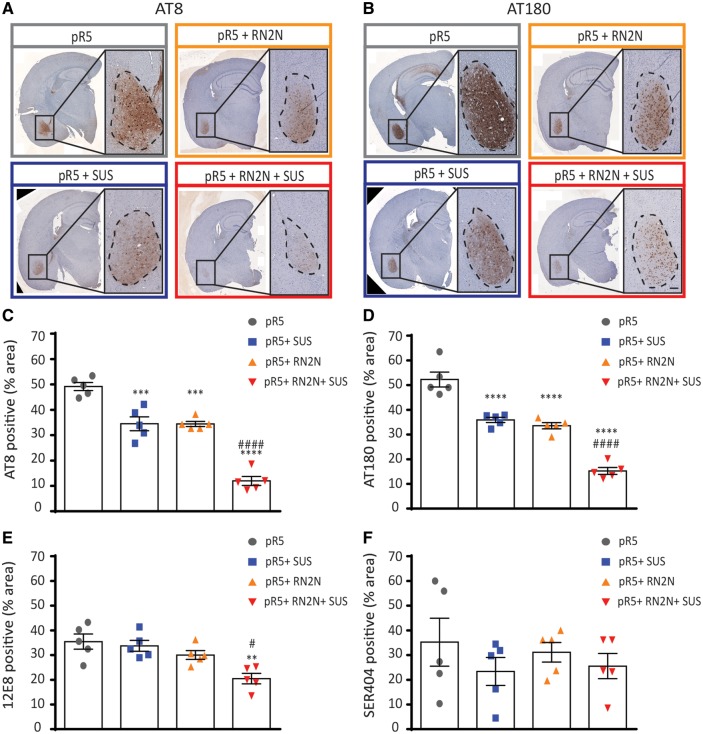
Figure 2.
Delivery of RN2N in combination with SUS significantly reduces phosphorylated tau levels in the amygdala. (A) Representative images of the AT8 phosphorylated tau immunoreactivity observed in a full brain section and amygdala of pR5 mice in each treatment group (Scale bar = 100 μm). (B) Representative images of the AT180 phosphorylated tau immunoreactivity observed in the amygdala of pR5 mice in each treatment group (Scale bar = 100 μm). (C) AT8 phosphorylated tau in the amygdala was significantly reduced in all treatment groups compared to the pR5 group (****P ≤ 0.0001). Comparison of the pR5 + RN2N + SUS group to the pR5 + SUS and pR5 + RN2N groups demonstrates a further reduction in AT8 tau-positive area in the amygdala (####P ≤ 0.0001). (D) AT180 phosphorylated tau in the amygdala was significantly reduced in all treatment groups compared to the pR5 group (****P ≤ 0.0001). Comparison of the pR5 + RN2N + SUS group to the pR5 + SUS and pR5 + RN2N groups demonstrates a further reduction in AT180 tau-positive area in the amygdala (###P = 0.0002). (E) 12E8 phosphorylated tau in the amygdala was significantly reduced in the RN2N + SUS group compared to the pR5 group (**P < 0.01), and was reduced in comparison to pR5 + SUS and pR5 + RN2N groups (#P ≤ 0.05). (F) Ser404 phosphorylated tau in the amygdala was not significantly reduced in any treatment group compared to the pR5 group (mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, n = 5).