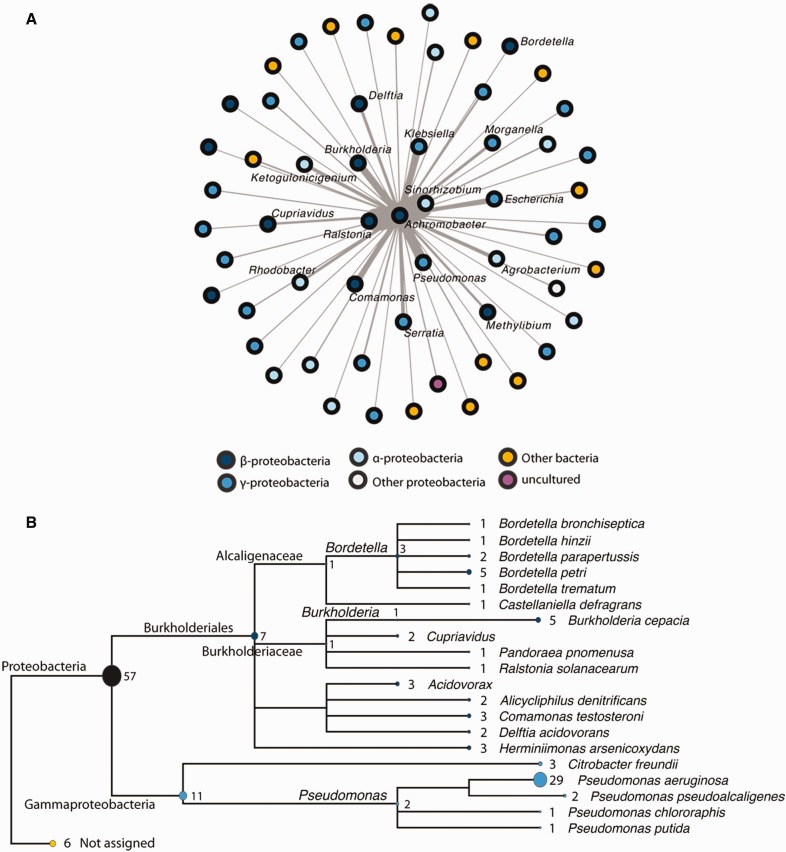
Fig. 6.—
Horizontal gene transfer between Achromobacter and other bacterial species. (a) Network showing the modules (five or more contiguous genes that match entries of the NCBI plasmid database and are present on the same strand) shared between Achromobacter isolates and other bacterial taxa. The color of each node reflects classification (grey to blue: different groups of proteobacteria; yellow: other bacterial species; violet: uncultured bacteria; outermost taxa labels were removed for clarity). A force-directed layout was used to draw the network so that the more a node is close to Achromobacter, the more it shares the same modules). (b) Tree showing the species with which putative mobile elements were exchanged. This analysis is based on a BLASTn search of Achromobacter DNA sequences (>5 kb) matching those of other bacterial species (>95% identity). MEGAN5 (Huson et al. 2007) was used to represent the BLAST results in the form of a tree. The ellipses’ width and the numbers next to them represent the number of sequences shared with each species/genus. The colours reflect classification, like in panel (a).