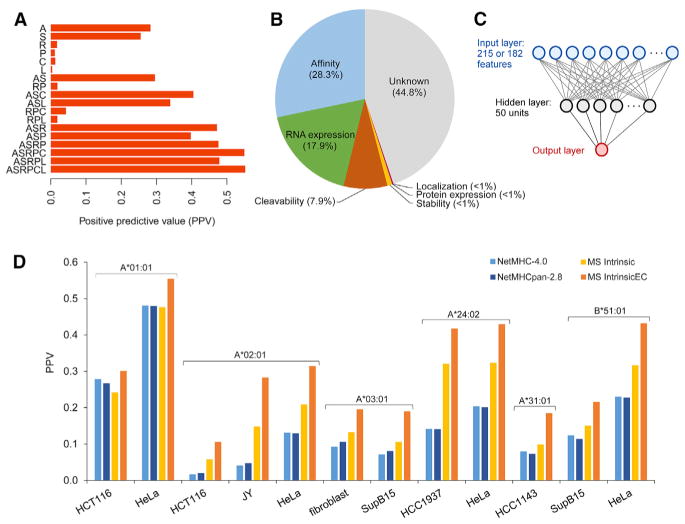
Figure 5. Evaluation of MS-Data-Based HLA-Peptide Binding Predictors.
(A) Positive predictive value of linear models used for discerning 9-mer MS peptides among a 999-fold excess of 9-mer decoys (averaging across 16 alleles). Models included one or more predictor variables (A = affinity, S = stability, R = RNA-Seq expression, P = protein expression (iBAQ), C = cleavability score, and L = source protein localization).
(B) Explanatory contributions of predictor variables derived from the cumulative improvement in predictive value as predictors are added.
(C) Cartoon representation of the neural-network model architecture. The 215 MSIntrinsic inputs included amino acid dummy variables (180 nodes), amino acid properties (27 nodes), and peptide properties (8 nodes). The 182 MSIntrinsicEC inputs included the amino acid dummy variables, expression (1 node), and cleavability (1 node).
(D) External evaluation. MS-binding data from two published datasets (Bassani-Sternberg et al., 2015; Trolle et al., 2016) were used for comparing the positive predictive value of MSIntrinsic and MSIntrinsicEC against NetMHCpan 2.8 and NetMHC 4.0 in identifying presented peptides among a 999-fold excess of random decoy 9-mers. Peptides were excluded from the evaluation if they were highly likely to bind an allele other than the one being evaluated. See also Figure S5.