Figure 1.
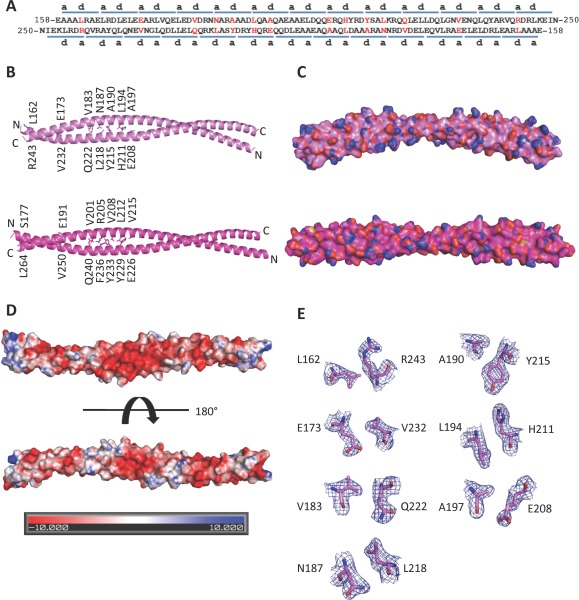
The BECN2 CCD. (A) Paired residues (red) of the two antiparallel monomers of the BECN2 CCD homodimer. The blue bars above or below the sequence indicate the heptad repeats of the BECN2 CCD. The letters a and d indicate the residues at the a and d positions of each heptad repeats, respectively. The nonideal interface pairs are colored red. (B) The X‐ray crystal structures of the BECN2 CCD (violet ‐ top) and the BECN1 CCD (magenta ‐ bottom) antiparallel homodimers. The side chains of nonideal interface residues are displayed in stick with atoms colored by type—oxygen red, nitrogen blue, and carbon violet (BECN2 CCD) or magenta (BECN1 CCD). (C) Surface representation, colored as in (B) of the BECN2 CCD homodimer demonstrates that it is a curved molecule with a radius of 15 nm in contrast to the straight rod‐like BECN1 CCD. (D) Electrostatic surface of the BECN2 CCD homodimer generated by APBS.40 The top panel shows the convex face and the bottom panel shows the concave face. (E) Atomic details of nonideal packing residues, color‐coded as in (B). The blue mesh represents the 2Fo–Fc electron density maps contoured at 1σ above the mean. This and other molecular figures were made using PyMOL (An interactive view is available in the electronic version of the article).41, 42
