Figure 1. Heterogeneity of depression and influences on susceptibility to depression.
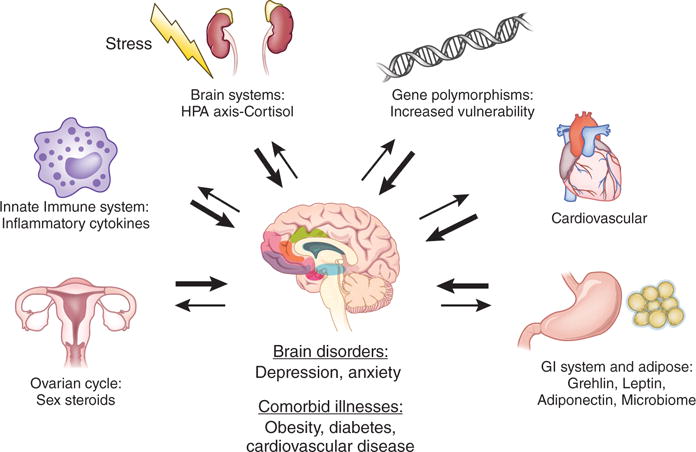
The heterogeneity of depression results from one or more pathological determinants. Notable effects include stress on brain neurotransmitter systems (NTs),activation of the HPA axis and cortisol, the innate immune system and inflammatory cytokines, fluctuations of ovarian steroids, the gastro intestinal (GI) system, adipose tissue and related peptides and microbiome, the cardiovascular system (e.g., VEGF or vascular endothelial growth factor), and gene polymorphisms that influence vulnerability and other organ systems as shown. These systems lead to increased incidence of depression as well as comorbid illnesses.
