Figure 6.
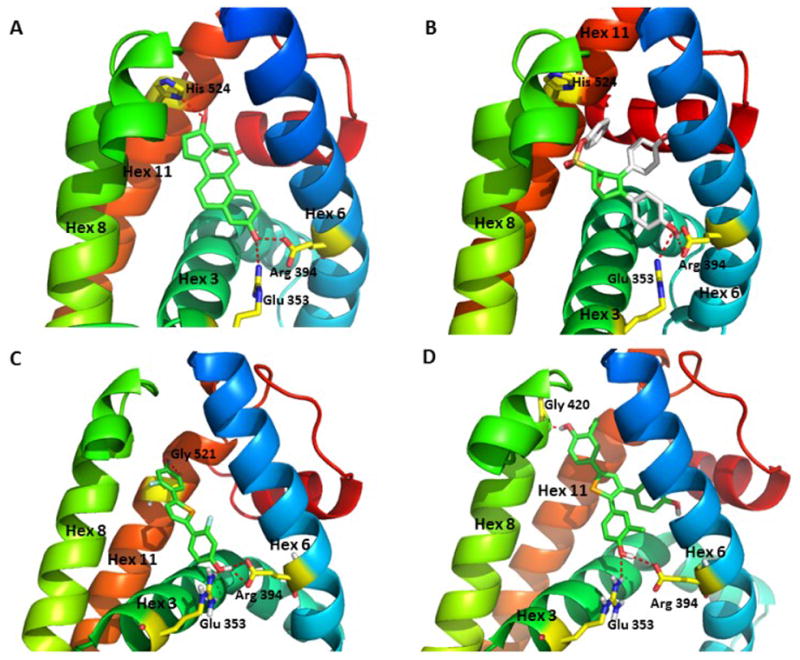
Model of selenophene ligands bound to ERα and comparisons with estradiol and OBHS. (A) Crystal structure of the ERα LBD in complex with E2 (PDB: 1ERE). The A-ring phenolic hydroxyl group of E2 forms hydrogen bonding interactions with helix 3 residue Glu353 and helix 6 residue Arg394, while the D-ring 17β alcohol interacts with the helix 11 residue His524. (B) Crystal structure of the ERα LBD in complex with oxabicyclic heptane sulfonate (OBHS) bound ERα. OBHS H-bonds to the conserved Glu353 and Arg394 residues. The phenyl sulfonate extends outward between helices 8 and 11.39 (C) Computer-developed model of 2f bound to ERα with conserved H-bonding to Glu353 and Arg394. The second phenolic group H-bonds to Gly521 on helix 11, which stabilizes helix 12 in the agonist conformation. (D) Computer-developed model of 8b bound to ERα with the conserved H-bonding to Glu353 and Arg394, and the second phenolic group with H-bonds to Gly420 on helix 8, avoiding the clash with helix 11.
