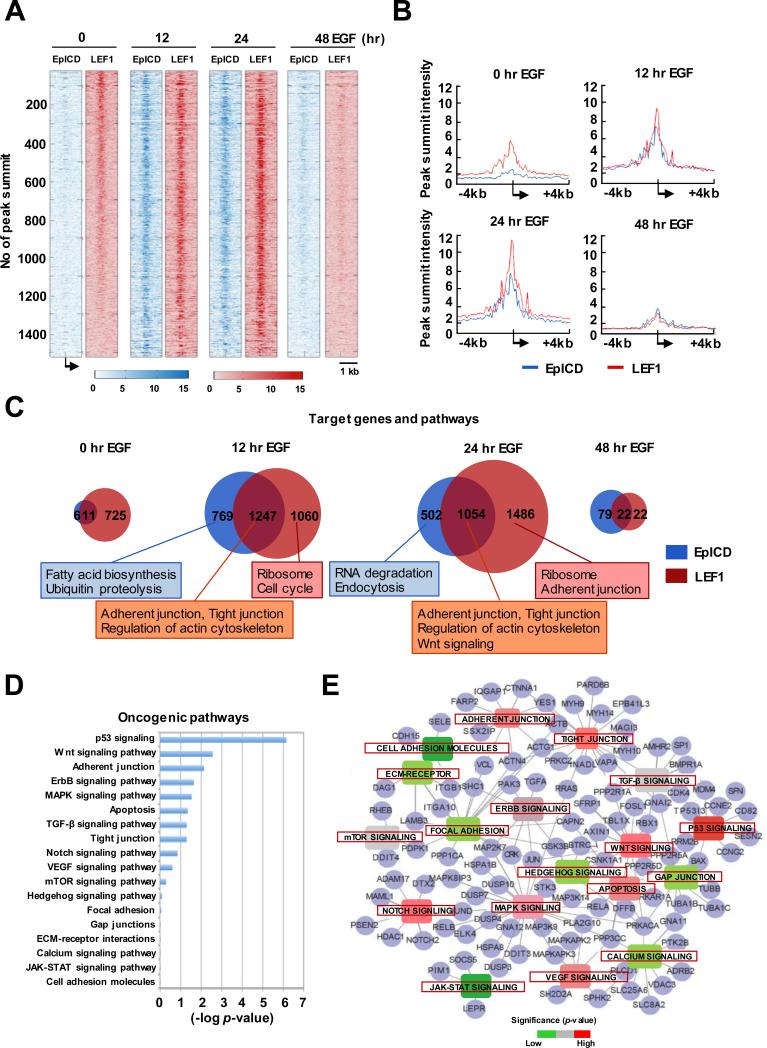
Figure 2.
Co-occupancies of EpICD and LEF1 in target loci involved in cell mobility functions. A, ChIP-seq peak summit alignments of EpICD and LEF1 in TSS regions in RL95-2 cells treated with EGF at different time points. Each row represents the same genes and the intensities of peaks are presented in colored scale bar. B, Peak summit intensity of target loci at different time points of EGF treatment. C, Venn diagrams of target loci and their biological functions at different time points of EGF stimulation. D, Oncogenic pathway analysis of 1247 EpICD-LEF1-regulated target loci. E, Interconnected signaling network of a subset of EpICD-LEF1-regulated target loci (n=105) involved in cell mobility functions.