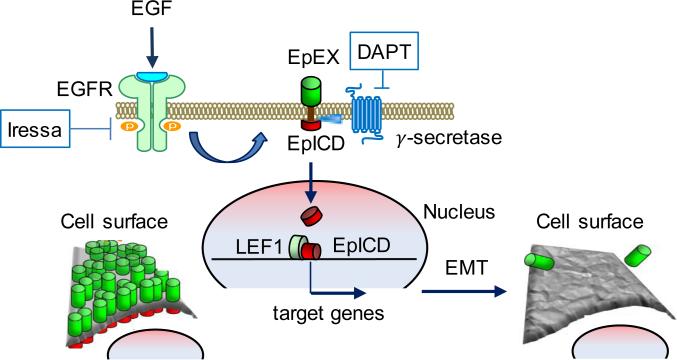
Figure 6.
A proposed model of cell response to the EGF treatment. EGF binding to an EGFR triggers cleavage of membrane EpCAM to the intracellular EpICD part that after nuclear translocation together with LEF1 targets expression of genes responsible for cell mobility. Simultaneous removal of the extracellular EpEX part reduces cell adhesion and increases cell elasticity. Therefore, both parts of the EpCAM molecule using distinct molecular mechanisms collaborate toward formation of the more invasive phenotype supporting tumor progression.