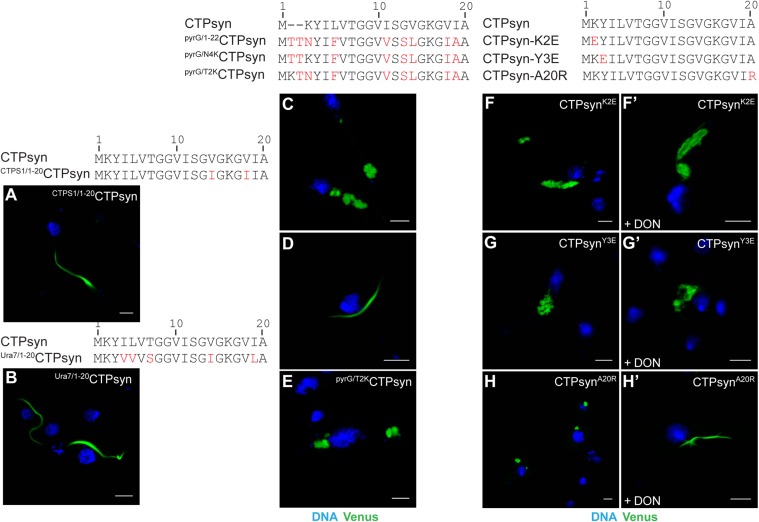
Fig. 3.
The conserved amino acid residues K2, Y3 and A20 at the CTP synthase N-terminus are necessary for filament assembly. Replacement of N-terminal 20 amino acids of the Drosophila CTPsyn with the corresponding human (CTPS1/1–20CTPsyn, A), S. cerevisiae (Ura7/1–20CTPsyn, B) and E. coli (pyrG/1–22CTPsyn, C) CTP synthase peptide shows that the bacterial sequence does not support cytoophidium formation. However, mutating the amino acid at position 4 (pyrG/N4KCTPsyn, D) but not position 2 (pyrG/N4KCTPsyn, E) to lysine residue (K) induces filament formation. The amino acid sequences (1–20) of the proteins are shown at the top of each panel with the amino acids different from the Drosophila CTPsyn marked in red. (F-H) Mutation of the Drosophila CTPsyn amino acids at position 2 (K2E), position 3 (Y3E) and position 20 (A20R) disrupts cytoophidium formation. CTPsynK2E and CTPsynY3E proteins form large clusters (F and G, respectively) while CTPsynA20R assembles into smaller cytoplasmic foci-like structures (H). In the presence of the CTPsyn inhibitor DON (F'-H') only CTPsynA20R protein assembles into a cytoophidium (H′). DNA stained with Hoechst is shown in blue while the Venus-tagged proteins are in green. Scale bar=5 µm.