Figure 4. CLASP2 is Necessary for Radial Migration of Cortical Projection Neurons in the Mammalian Brain.
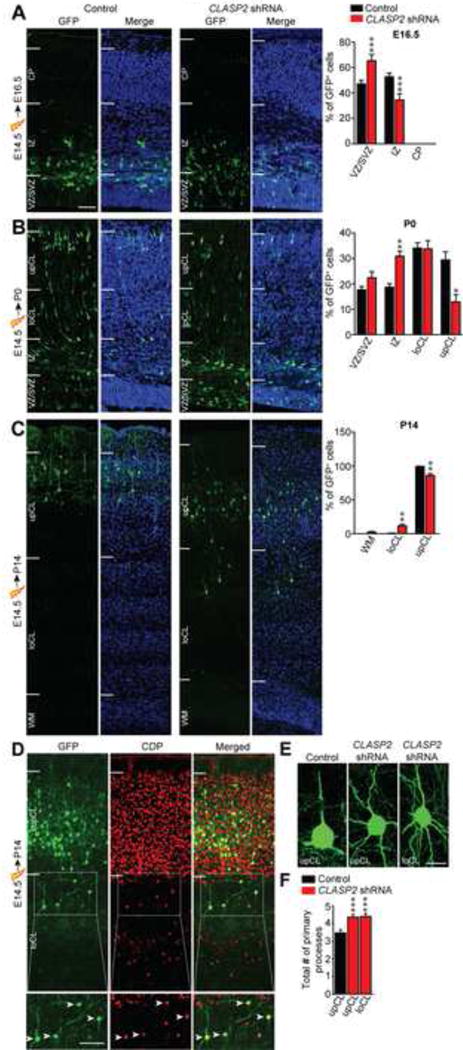
(A–C) Mouse embryos were electroporated in utero with GFP-tagged CLASP2 shRNAs or scrambled control at E14.5 and analyzed at E16.5 (A, control, n = 6 brains; CLASP2 shRNA, n = 6 brains), P0 (B, control, n = 3 brains; CLASP2 shRNA, n = 6 brains) and P14 (C, control, n = 4 brains; CLASP2 shRNA, n = 6 brains). Coronal sections of the cortex were visualized for transfected GFP-positive neurons (green) and cell nuclei (Hoeschst 33342, blue). White lines indicate the demarcations for different cortical regions (VZ = ventricular zone, SVZ = subventricular zone, IZ = intermediate zone, CP = cortical plate, loCL = lower cortical layer, upCL = upper cortical layer, WM = white matter). For additional data, see Figure S3.
(D) Coronal brain sections from E14.5 CLASP2 shRNA electroporation and analyzed at P14 were immunostained with layers II/III marker CDP (red).
(E–F) Representative images of morphological defects of CLASP2 shRNA neurons in the upCL and loCL. CLASP2 knockdown caused an increase in the number of primary neurites independent of cortical layer (control, n = 53 cells; CLASP2 shRNA upCL, n = 60 cells; CLASP2 shRNA loCL, n = 39 cells were analyzed). For additional data, see Figure S4.
Data are means ± SEM and statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001). Scale bar represents 50 μm (A–D) and 10 μm (E).
