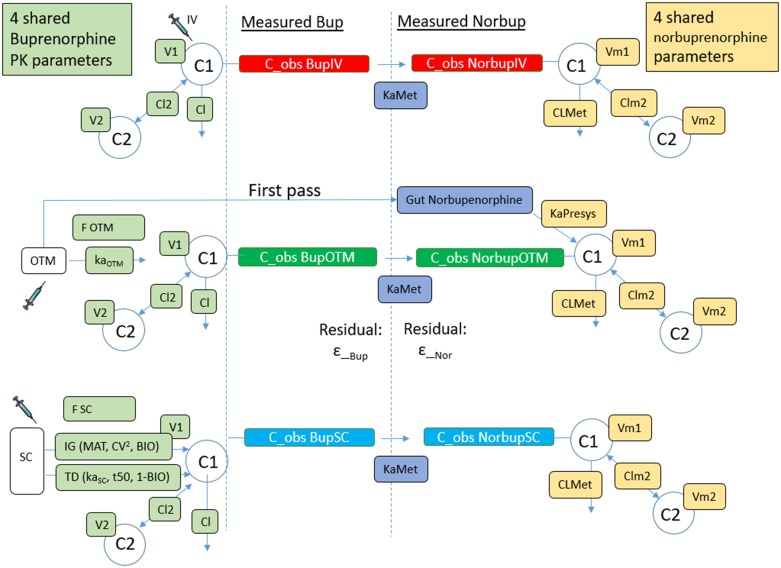
Fig 2. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model representation for buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine after subcutaneous, intravenous and buccal administration in six cats.
For the SC route, combined Inverse Gaussian (IG, rapid but short lasting) and Time-dependent (TD, delayed and progressive onset) inputs. Buprenorphine central PK parameters; clearance (CL), volume of distribution of the central compartment (V1), intercompartmental clearance (CL2), volume of distribution of peripheral compartment (V2). Norbuprenorphine central PK parameters: clearance (CLMet), volume of distribution of the central compartment (V1Met), intercompartmental clearance (CL2Met) and volume of distribution of the peripheral compartment (V2 Met). Rate constant of transformation from parent to metabolite (KaMet), first pass norbuprenorphine absorption rate (Kafirst-pass). PK parameters specific to OTM route: bioavailability (FOTM, parent and metabolite), absorption rate constant (kaOTM). PK parameters specific to SC route: bioavailability (FSC), proportion taken by IG input (BIO) and time-dependent delayed input (1-BIO), mean input rate time (MAT) was 7.21 h (3.5%) and variance of the input time (CV), maximal absorption rate constant (kaSC), time to achieve 50% of this maximum rate (T50).