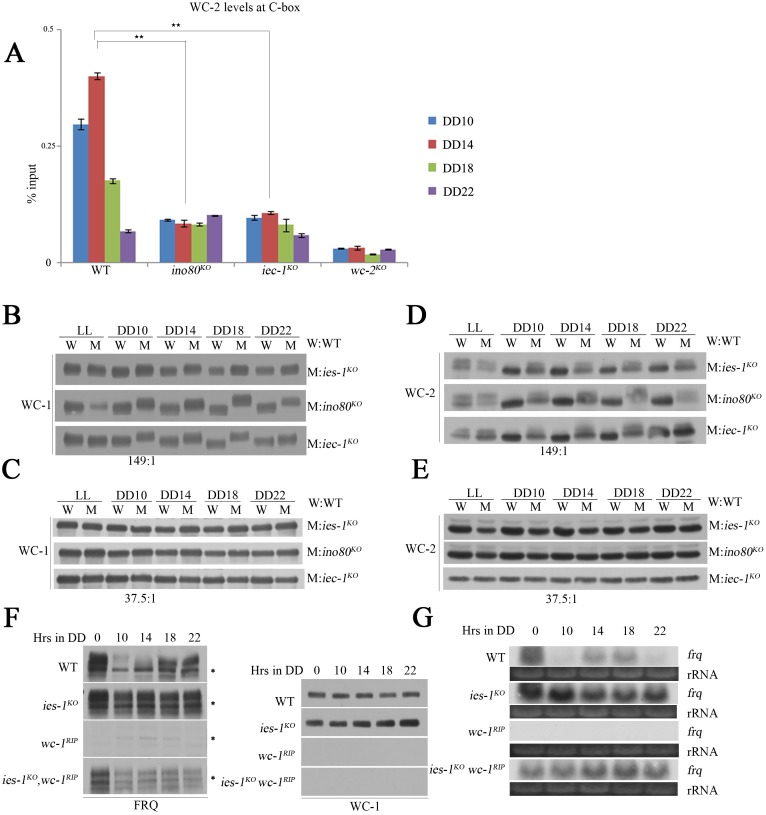
Fig 4. The INO80 complex is required for the suppression of WC-independent frq transcription.
(A) ChIP analysis showing WC-2 enrichment at the C-box in the wild-type, ino80KO, iec-1KO, and wc-2KO (bd) strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. Significance was assessed by two-tailed t-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Error bars show the mean ±S.D. (n = 3). (B) Western blot analysis showing the phosphorylation of WC-1 in the wild-type, ies-1KO, ino80KO and iec-1KO strains. The numbers indicate the ratio of acrylamide/bisacrylamide used in the SDS-PAGE gel. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. (C) Western blot analysis showing the levels of WC-1 in the wild-type, ies-1KO, ino80KO and ies-1KO strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. (D) Western blot analysis showing the phosphorylation of WC-2 in the wild-type, ies-1KO, ino80KO and ies-1KO strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. (E) Western blot analysis showing the levels of WC-2 in the wild-type, ies-1KO, ino80KO and ies-1KO strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. (F) Western blot analysis of FRQ or WC-1 in the wild-type, ies-1KO, wc-1RIP (bd), and ies-1KO wc-1RIP strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media. (G) Northern blot analysis showing the levels of frq mRNA in the wild-type, ies-1KO, wc-1RIP (bd), and ies-1KO wc-1RIP strains. The strains were grown in 2% glucose liquid media.