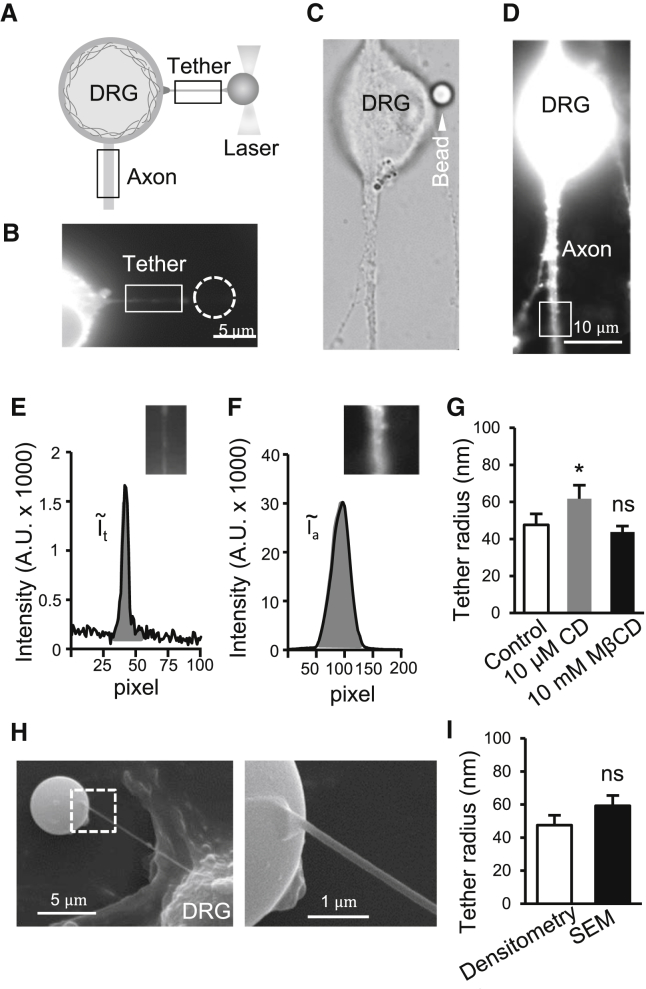
Figure 5.
Measurement of the radii of membrane tethers by fluorescent densitometry. (A) Schematic diagram illustrates procedures of measuring the radii of membrane tethers by fluorescent densitometry. DRG neurons are prelabeled with the fluorescent dye DiI. Fluorescent intensities in a segment of tether (boxed region) and a segment of axon (boxed region) of a neuron are measured and used for fluorescent densitometry. (B) Image shows a membrane tether pulled out from a DRG neuron prelabeled with DiI. (C) Bright field image of the DiI-labeled DRG neuron and the proximal segment of its axon. The cell is the same one shown in (B) before the tether was pulled out. The arrowhead indicates the bead used for pulling the membrane tether as in (B) before the tether was pulled out.. (D) Same as (C), except the fluorescent image of the cell was taken. (E) Graph shows DiI fluorescent intensity of the unitary length (100 pixels) across the membrane tether in the boxed region. The area under the curve (shaded) is the integrated fluorescent intensity of the membrane tether segment (ĩt). (F) Graph shows DiI fluorescent intensity of the unitary length (100 pixels) across the axon in the boxed region. The area under the curve (shaded) is the integrated fluorescent intensity of the axon segment tether (ĩa). (G) Tether radii determined by the fluorescent densitometry for DRG neurons under control condition (open bar), after the treatment of cells with 10 μM CD to disrupt actin filaments (shaded bar), or with 10 mM MβCD to sequester membrane cholesterol (solid bar). (H) SEM images of a membrane tether pulled with a bead from a DRG neuron in normal bath solution. (Left panel) Image at 10,000× showing the membrane tether, the bead, and a small portion of the DRG neuron. (Right panel) Image at 40,000× showing a portion of the bead and the tether. (I) Summary data comparing membrane tether radii measured by the fluorescent densitometry method (open bar) and the SEM method (solid bar). Data represent mean ± SE, ∗p < 0.05; ns, not significantly different.