Figure 1.
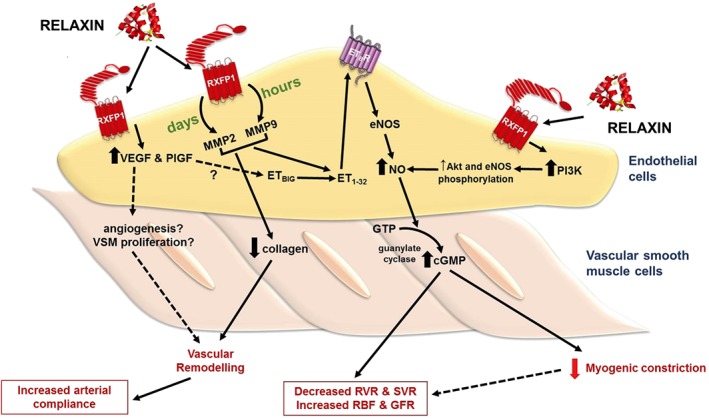
Effects of relaxin treatment in small renal arteries. Relaxin administration for hours and days increases MMP activities in ECs, leading to the conversion of big ET to ET1–32, which activates endothelial ETB receptors. Stimulation of endothelial ETB receptors causes NO production and activates smooth muscle soluble guanylate cyclase, leading to cGMP accumulation and vasodilation. Vasodilation of small renal arteries reduces myogenic reactivity and renal vascular resistance (RVR) and increases renal blood flow (RBF) and GFR. Relaxin also directly acts on endothelial RXFP1 receptors to increase PI3 kinase‐dependent Akt‐eNOS phosphorylation, resulting in NO production. In addition to vasodilation, relaxin treatment causes vascular remodelling in the small renal arteries. Relaxin treatment increases angiogenic factors such as VEGF and PlGF, and reduces collagen content, causing vascular remodelling and increases arterial compliance. SVR, systemic vascular resistance.
