Figure 7.
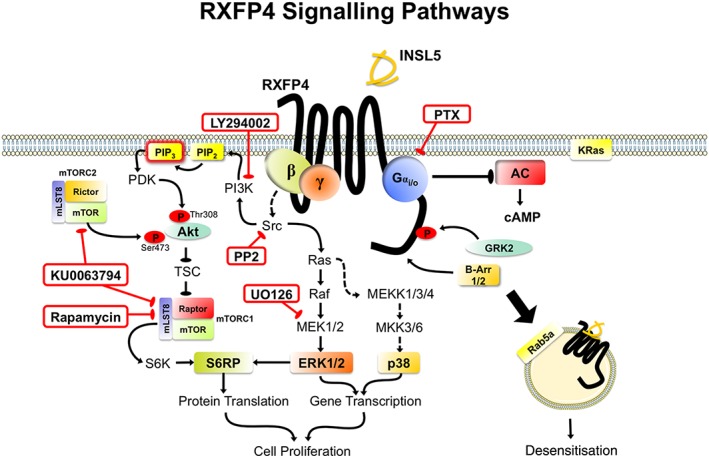
RXFP4 receptor signal transduction pathways. Inhibitors used in studying RXFP4 receptor signalling mechanisms are boxed in red. Following INSL5 stimulation, RXFP4 receptors recruit multiple Gαi/o subunits (predominantly GαoA, GαoB, Gαi2) that activate a range of signalling pathways, including cAMP inhibition, ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), Akt (Thr308/Ser473) p38MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) and S6RP (Ser235/236) via intermediary pathways such as mTORC1/C2, Src, PI3K and MEK1/2, leading to enhanced cell proliferation. Activated RXFP4 receptors interact with GRK2 and β‐arrestins (β‐Arr 1/2), which leads to movement of the receptor away from the plasma membrane into early endosome compartments. Note: speculative pathways are shown with dotted lines. mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR; phosphoinositide‐dependent kinase, PDK.
