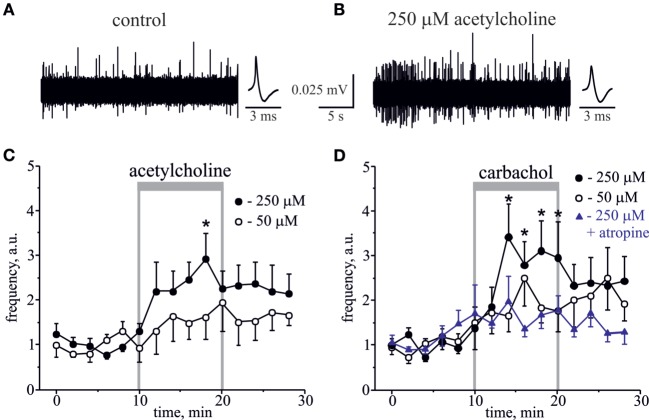
Figure 1.
Action of acetylcholine (ACh) and carbachol on nociceptive firing in the meningeal trigeminal nerves. (A) Representative traces of trigeminal nociceptive firing and average spike shape in control conditions and (B) during application of 250 µM ACh. (C) The time-course of changes of nociceptive spike frequency during application of 50 and 250 µM ACh. (D) The time-course of changes of nociceptive spike frequency during application of 50 and 250 µM carbachol and 250 µM carbachol in the presence of 1 µM atropine. Each time point represents a mean spike frequency for 2 min of recording (mean ± SEM, n = 6–10, one-way repeated measures ANOVA, Tukey test, *p < 0.05).