Figure 1.
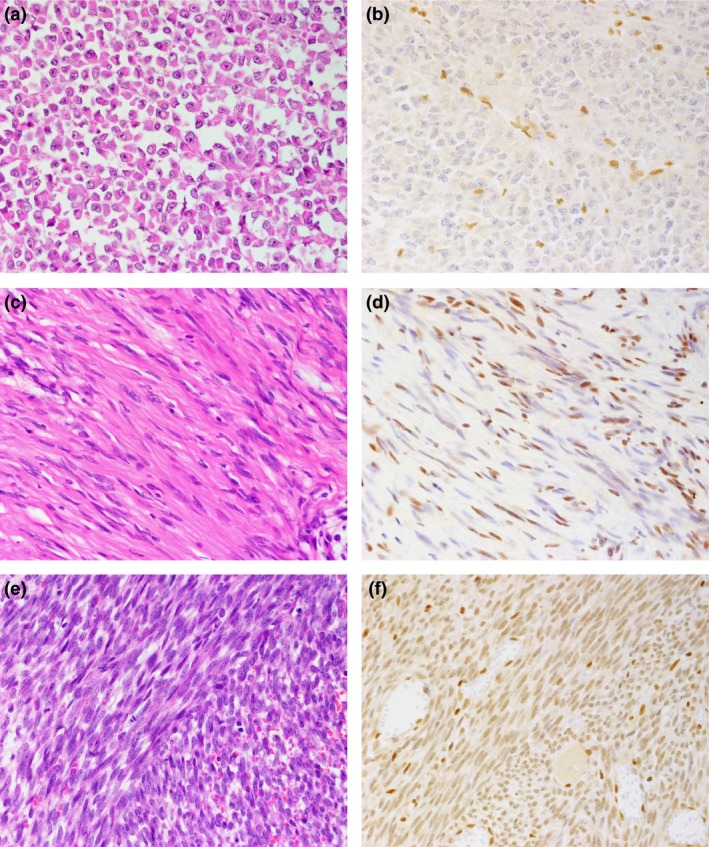
Hematoxylin–eosin histologic (a, c, e) and SMARCB1/INI1 (b, d, f) immunohistochemical findings. (a, b) Malignant rhabdoid tumor (2‐year‐old male; kidney). No nuclear expression of SMARCB1/INI1 protein is observed in tumor cells, whereas infiltrating lymphocytes or vascular endothelial cells disclose immunoreactivity (b). (c, d) Schwannomatosis (48‐year‐old woman; cauda equina). SMARCB1/INI1 protein expression is focally reduced with a mixture of nuclear‐positive and nuclear‐negative tumor cells, showing mosaic pattern (d). (e, f) Synovial sarcoma (22‐year‐old woman; abdominal wall). The tumor cells showed reduced expression of SMARCB1/INI1 protein compared with the positive control, which included infiltrating lymphocytes and entrapped normal tissue (f).
