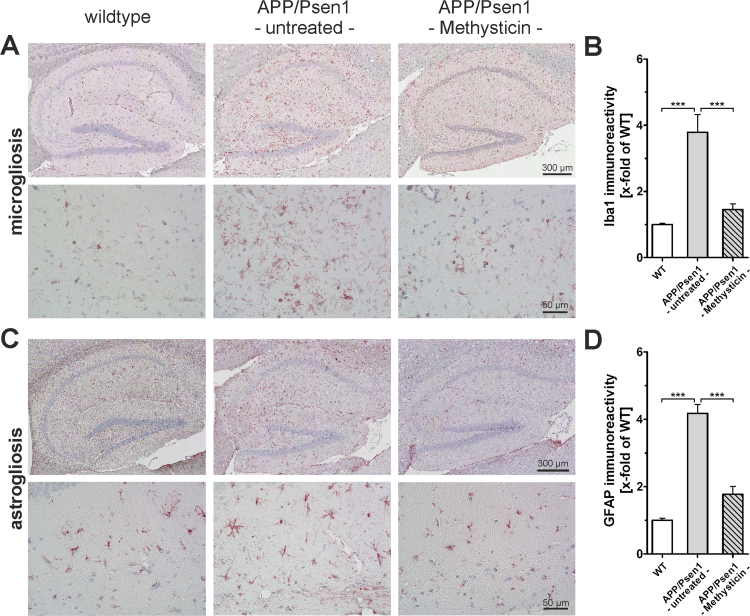
Fig. 5.
Neuroinflammation in hippocampi of APP/Psen1 mice is reduced by methysticin treatment. (A & C) Microglia infiltration and astrogliosis was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining against Iba1and GFAP respectively (n=6). Pictures were generated by scanning the hippocampus at 20× magnification and subsequent merging of these pictures to a single picture. The upper lanes in A and C show representative pictures of wild type (1st column), untreated APP/Psen1 (2nd column) and methysticin-treated APP/Psen1 (3rd column) mouse hippocampi. The lower lanes in A and C provide detailed pictures at 40× magnification of the same groups. Scale bars: upper lanes=300 µm, lower lanes =50 µm. (B & D) Quantification of immunoreactivity of 3 consecutive sections of each hippocampus. Untreated APP/Psen1 mice showed prominent microglia infiltration and astrogliosis that was extensively elevated compared to wild type (WT) mice. Methysticin application led to a significant reduction of microglia infiltration as well as astrogliosis in these animals. (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison post hoc test). Data represent mean+SEM; n=6; *** p<0.001 as indicated in the chart.