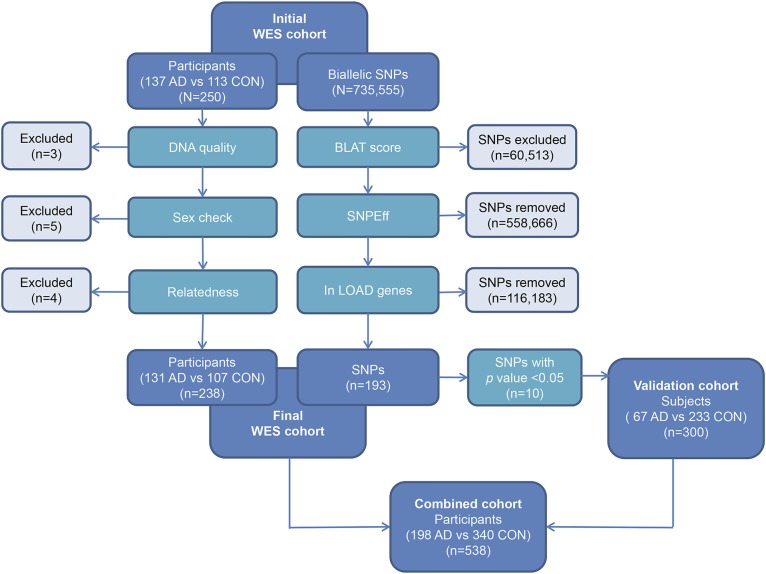
Figure 1. Study design.
Whole-exome sequencing (WES) sample quality control (QC) led to exclusion of samples with poor sequence quality, sex ambiguity, or cryptic relatedness. WES single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) QC led to exclusion of SNPs with a BLAST-like alignment tool (BLAT) score >1, those not resulting in an alteration of the coding sequence, and those outside the 20 late-onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD) genome-wide association study loci candidate genes. Of the remaining 193 variants tested in the final post-QC WES cohort (n = 238), 10 demonstrated association with Alzheimer disease (AD) risk with an uncorrected p < 0.05. After excluding 2 SNPs with strong linkage disequilibrium, the remaining 8 SNPs were confirmed by sequencing or genotyping in an independent validation cohort (n = 300). These 8 SNPs were also evaluated in the combined cohort (n = 538).