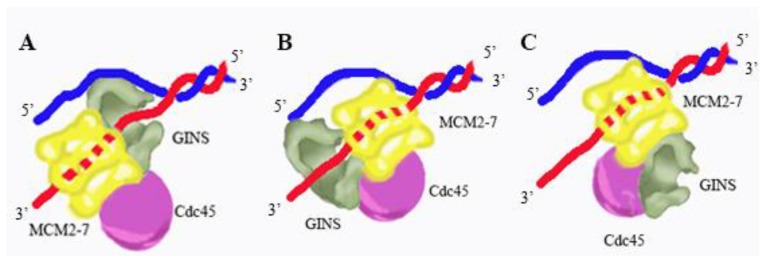
Figure 7.
Model for CMG replicative helicase architecture at a fork. Three different models for CMG replicative helicase architecture at a fork are shown. In each of these models, CMG unwinds DNA by a steric exclusion mechanism. (A) in model A, GINS is positioned at the front of the fork, gripping single-stranded DNA and presenting the ssDNA to the Mcm2-7 ATPase; (B) in model B, GINS is positioned at the back of the fork, gripping leading strand DNA as it exits from the Mcm2-7 complex; and (C) in model C, GINS is at the side of the Mcm2-7 complex and GINS does not bind fork DNA under normal conditions. Recent electron microscopy studies suggest that Model C is relevant for a replication fork under normal conditions.