Fig. 5.
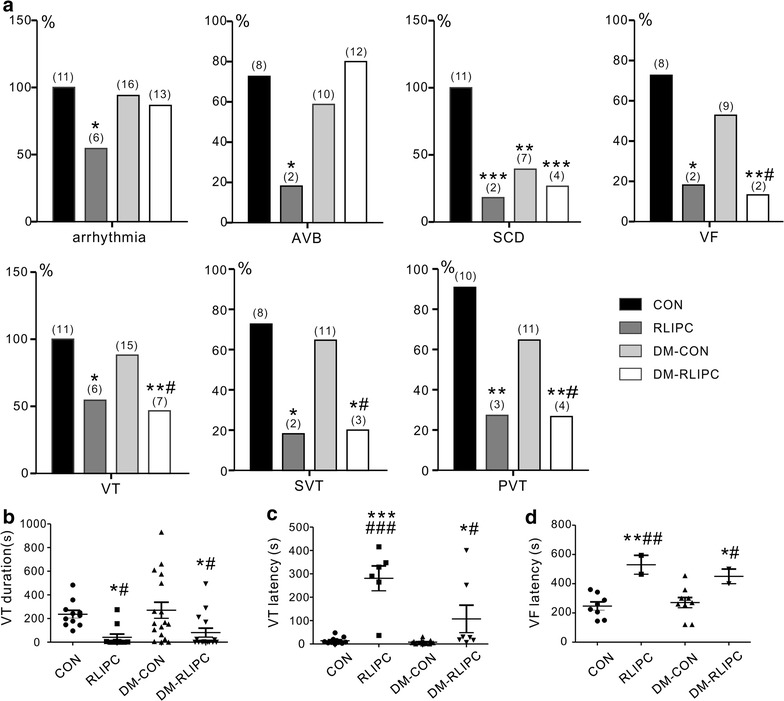
RLIPC confers differential cardioprotection against post-cardiac IRI arrhythmias and SCD in diabetic versus non-diabetic STZ-diabetic rats. a Quantification of arrhythmias during myocardial IRI in diabetic or nondiabetic rats with or without RLIPC (n = 11–17). Numbers of animals per category are indicated in parentheses. AVB AV block, SCD sudden cardiac death, VF ventricular fibrillation, VT ventricular tachycardia, SVT sustained ventricular tachycardia, PVT polymorphic VT, CON control, RLIPC remote liver ischemia conditioning, DM STZ-induced diabetes.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. CON, # P < 0.05 vs. DM-CON. b Mean VT durations for non-diabetic or STZ-induced diabetic rats with or without RLIPC (n = 11–17). Rats without VT were indicated as 0 s duration. *P < 0.05, vs. CON, # P < 0.05 vs. DM-CON. c, d Latency to first run of c VT or d VF after the onset of reperfusion in non-diabetic or STZ-induced diabetic rats with or without RLIPC (n = 11–17). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 vs. CON, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 and ### P < 0.001 vs. DM-CON
