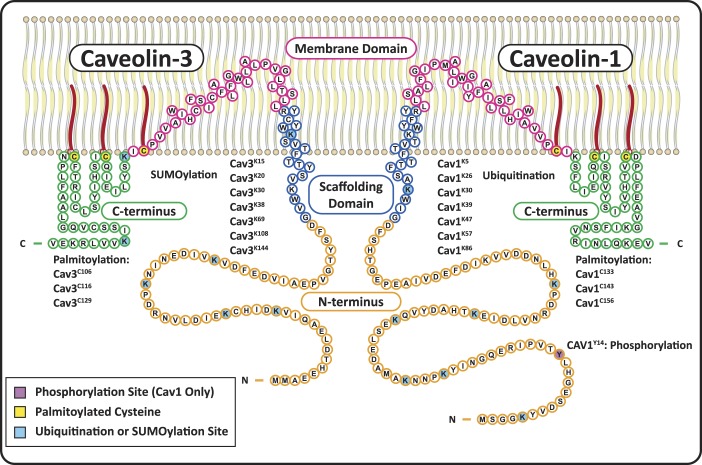
Fig. 1.
Structure and posttranslational modifications of caveolin-1 (Cav1) and caveolin-3 (Cav3). Cav1 and Cav3 have four primary domains: NH2-terminal domains (orange) with multiple ubiquitination/SUMOylation sites on both Cavs, as well as a phosphorylation site on Cav1; scaffolding domains (blue) that form α-helices and are inserted into the membrane, with a cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) composed of the eight residues proximal to the membrane domain; helix-turn-helix membrane domains (fuchsia) that exit the membrane at a palmitoylation site; and COOH-terminal domains (green) with two more palmitoylated cysteines and two SUMOylation sites on Cav3.