Fig. 5.
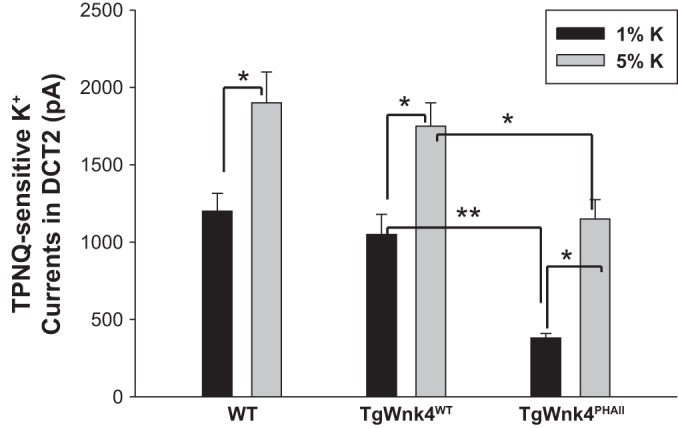
High-K+ intake stimulates ROMK in DCT2/CNT. A bar graph summarizes the effect of high dietary K intake (5%) for 7 days on TPNQ-sensitive K+ currents in the DCT2/CNT of WT, TgWnk4WT, and TgWnk4PHAII mice. TPNQ (400 nM)-sensitive ROMK currents in DCT2/CNT were measured at −40 mV. The statistical significance is indicated by *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01.
