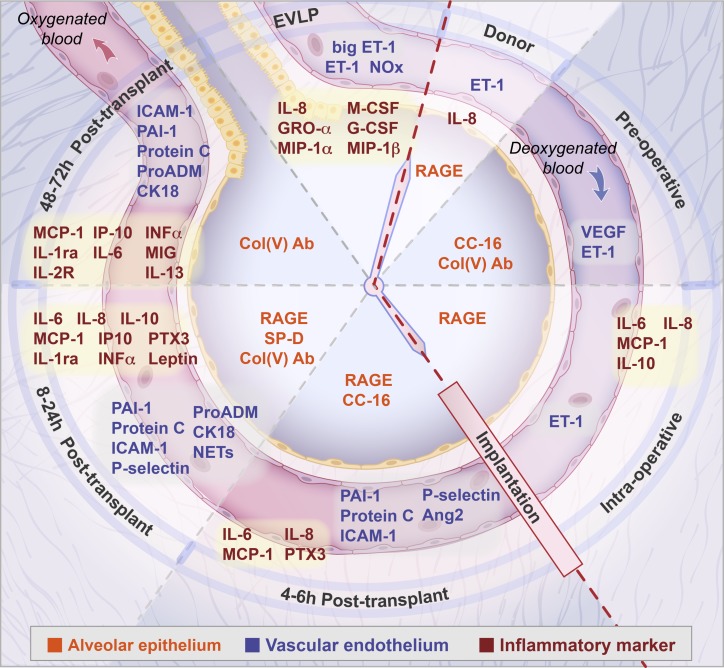
Fig. 1.
Representation of the time course, including ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP), from the donor through to the postoperative period (clockwise direction), of biomarkers associated with primary graft dysfunction in the recipient. Biomarkers specific to the epithelium are shown centrally in the alveolus (orange print). Biomarkers specific to the vascular endothelium as well as coagulation, fibrinolysis, platelet activation, hypoxic injury, cell death markers and neutrophil activation are shown in the capillary lumen (blue print). Inflammatory cytokines are in red print. Epithelial markers: RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; CC-16, club cell secretory protein; col(V), antibodies to collage type V; SP-D, surfactant protein D. Endothelial markers: ET-1, endothelin; big ET-1; NOx, nitric oxide metabolites; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; Ang-2, angiopoietin 2; ICAM-1, intracellular adhesion molecule-1. Marker of hypoxic injury: proADM, proadrenomedullin. Cell death marker: CK18, cytokeratin 18. Marker of neutrophil activation: NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps. Markers of coagulation and fibrinolysis: PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; protein C. Marker of platelet activation: P-selectin. Markers of inflammation: IL, interleukin-6, 8, 10, 13, 1ra, and 2R; M-CSF, macrophage colony stimulating factor; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; GRO-A, growth-regulated oncogene; MIP-1α and -1β, macrophage inflammatory protein-1α and -1β; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein; PTX3, long pentraxin-3; INF-α, interferon-α; IP, interferon-γ; MIG, monokine induced by interferon-γ.