Fig. 1.
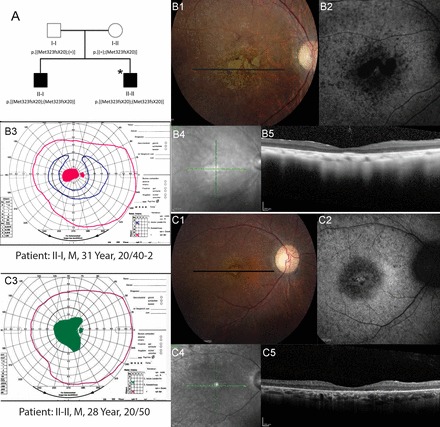
Pedigree and phenotype of 2 siblings with CERKL mutations. A: pedigree with homozygous 2 base pair deletion (c.967_968delAT, p.Met323Val fsX20) in CERKL gene. *Individuals who underwent whole exome sequencing. Clinical features of affected members with CERKL mutations. B1 and C1: color fundus photos; B2 and C2: fundus autofluorescence; B3 and C3: Goldmann visual fields; pink lines indicate the V4e isopter, green lines show the II4e isopter in a patient who was unable to perceive the I4e target, and blue lines show the I4e isopter. Black lines on color photos indicate location of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) scans. Homozygotes show heterogeneous, increased autofluorescence (AF) around the fovea; SD-OCT shows severe outer retinal layer loss; visual fields demonstrate central scotomas. B4 and C4: infrared fundus photos; B5 and C5: optical coherence tomography scans.
