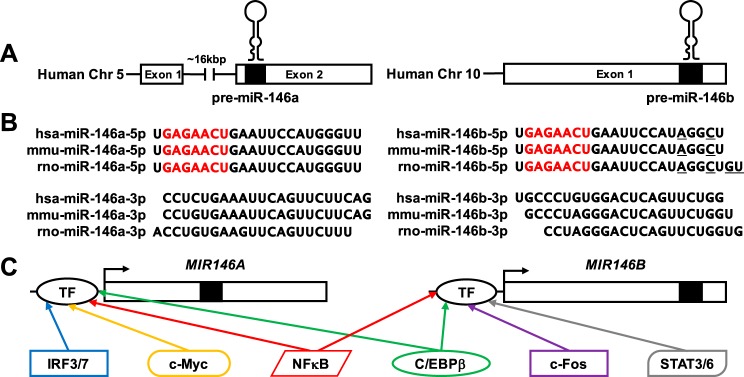
Fig. 1.
The microRNA (miR)-146 family consists of 2 members, miR-146a and miR-146b, found on human chromosomes 5 and 10, respectively (A). Basic exon structure for the human genes is shown, with black boxes and hairpin structures indicating the location of the precursor miR-146 sequences. B: sequences for the mature -5p and -3p strands are shown for both miR-146a and miR-146b in human, mouse, and rat. There is high sequence homology across species for miR-146a-5p and miR-146b-5p, respectively. Note that miR-146a-5p and miR-146b-5p differ by only a few bases on the 3′-end in each species (nucleotides differing between miR-146a-5p and miR-146b-5p are underlined). While the -3p sequences for both miR-146a and miR-146b, respectively, are largely homologous across species, within each species the miR-146a-3p and miR-146b-3p sequences are nonhomologous. C: a schematic of predicted and known transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the promoter regions of both MIR146A and MIR146B.