Fig. 2.
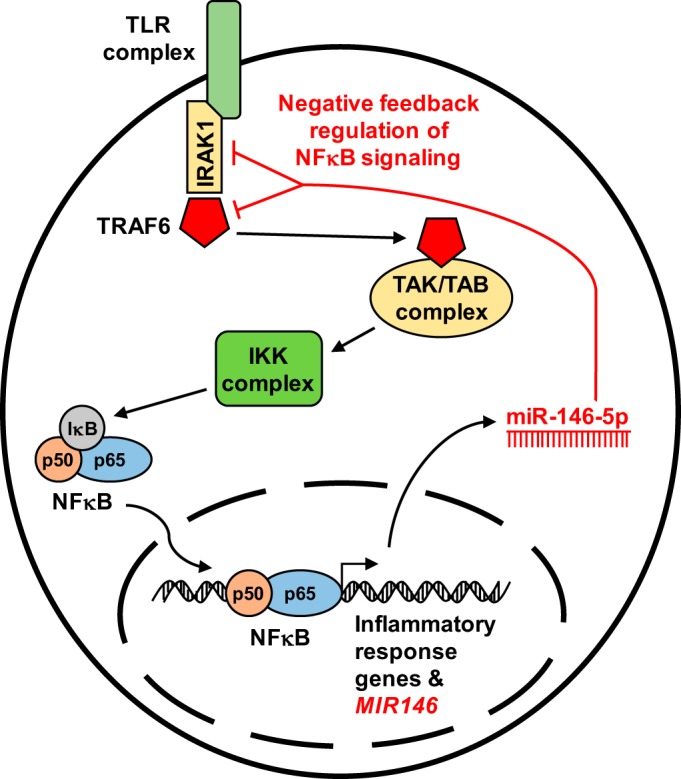
A large majority of miR-146 literature focuses on the innate immune and inflammatory responses mediated by NF-κB signaling. miR-146 has been shown to act as a negative feedback regulator of NF-κB signaling by suppressing the translation of 2 targets: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). Stimulation of the toll-like receptor complex (TLR) leads to the association of IRAK1 and TRAF6 with the TAK/TAB complex, resulting in the subsequent activation of the IKK complex and translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus where it induces expression of inflammatory/immune response genes and induces expression of miR-146. miR-146 then may act as a molecular brake on NF-κB signaling by suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6 expression.
