Figure 3. Proposed mechanism for photoredox catalytic α-carboxylation of amines with CO2.
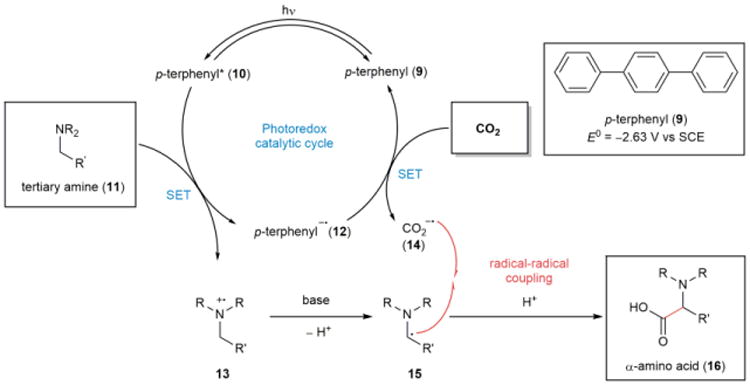
The excited singlet state of the photoredox catalyst p-terphenyl (10) is quenched by tertiary amine 11, and the radical anion of p-terphenyl (12) reduces CO2 to its radical anion (14). After the deprotonation of amine radical cation 13 to afford α-amino radical 15, radical-radical coupling of 14 and 15 provides α-amino acid 16.
