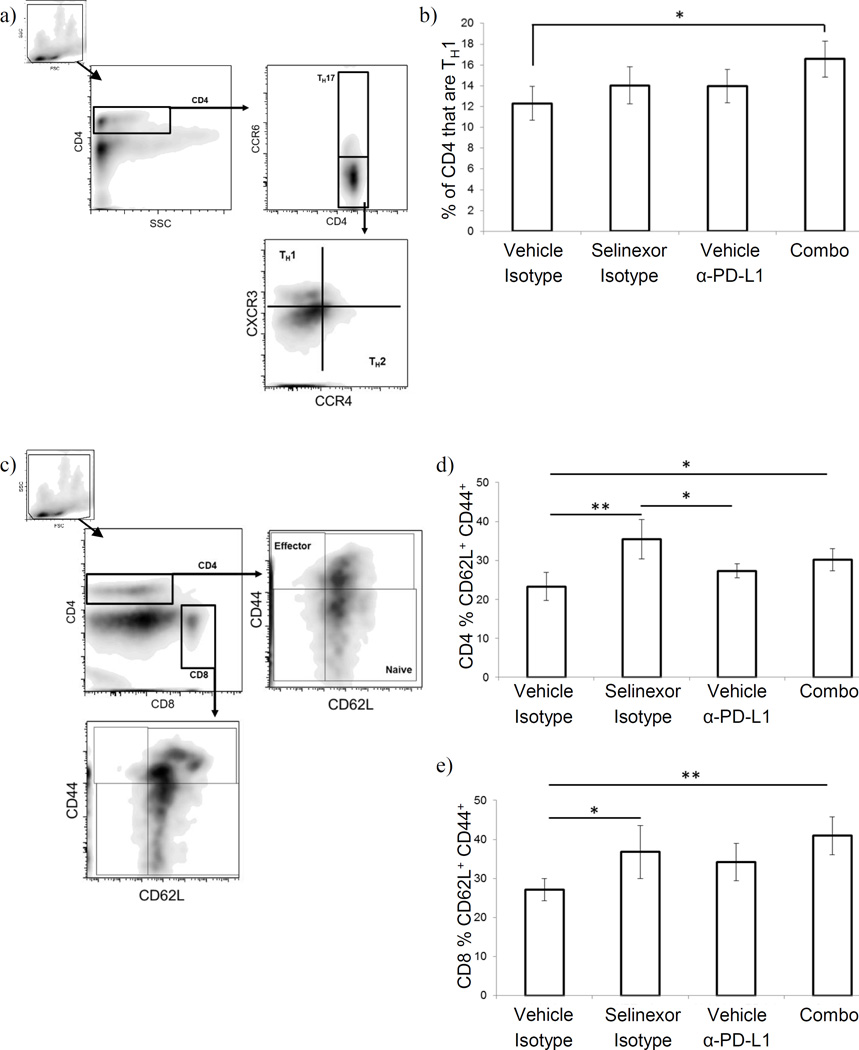
Figure 4. Selinexor + anti-PD-L1 antibodies induce T cell activation and TH1 differentiation in melanoma bearing animals.
(a–b) Helper T cells were quantified on the basis of their pattern of chemokine receptor expression. (a) gating strategy: CD4+ viable cells (based on forward/side scatter and anti-CD4) were gated based on CCR6 expression: CCR6+ cells were defined as TH17, while CC6− cells were further gated based on expression of CXCR3 (TH1 cells) and CCR4 (TH2 cells). (b) Proportion of TH1 cells among splenic CD4+ T cells. (c–e) T cell activation status was assessed on the basis of cell surface phenotype. (c) gating strategy: singly positive CD4+ or CD8+ viable cells (based on forward/side scatter and anti-CD4 and anti-CD8) were selected and identified as a naïve, early activated/central memory, or effector phenotype based on staining for CD44 and CD62L. (d & e) Proportion of CD4+ T cells (d) or CD8+ T cells (e) with an early activated/central memory phenotype (CD62L+ CD44+). n=5–6 mice per group; Mean ± S.D.; *, p<0.05 between indicated groups.