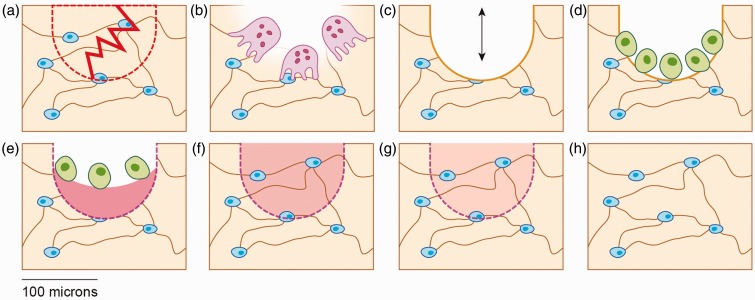
Figure 1.
Schematic of bone remodeling following fatigue damage in trabecular bone. (a) Linear microcrack disrupting the osteocyte lacunocanalicular system, leading to osteocyte apoptosis in the affected area (dotted region). (b) Osteoclastic resorption of microdamaged bone. (c) Temporary negative bone space due to osteoclastic resorption. (d) Osteoblast recruitment to the remodeling space. (e) Osteoblastic deposition of unmineralized bone matrix (osteoid). (f) Primary mineralization of newly deposited matrix. (g) Secondary mineralization of bone matrix. (h) Completed remodeling cycle. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)