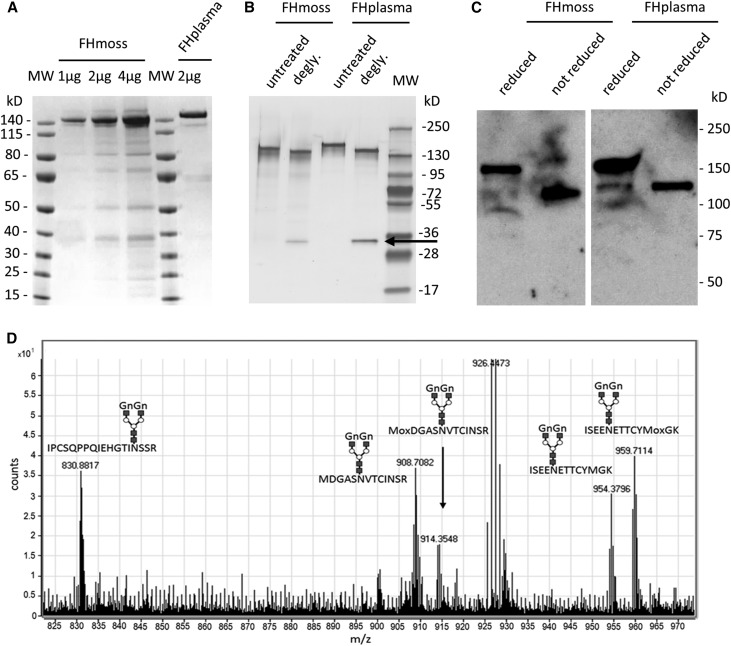
Figure 1.
Purified FHmoss is intact and completely N-glycosylated. (A) Characterization of FHmoss and FHplasma. Samples were separated under reducing conditions on SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained. (B) Deglycosylation (degly.) of FHmoss and FHplasma. Samples treated with PNGase F (arrow) and untreated controls were separated under reducing conditions on SDS-PAGE and silver stained. MW, molecular mass marker. (C) Western blot of FHmoss and FHplasma under reducing and nonreducing conditions. (D) Summed MS1 scans showing complex GnGn-glycosylated FHmoss peptides. FHmoss was tryptically digested and analyzed by nano–LC-MS/MS on a Q-TOF instrument. Among the identified peptides, the glycopeptides 850–867 (IPCSQPPQIEHGTINSSR; glycosylation site Asn864), 889–901 (ISEENETTCYMGK; glycosylation site Asn893), and 1006–1018 (MDGASNVTCINSR; glycosylation site Asn1011) are displayed. Oxidized methionine is labeled with Mox. Shown m/z values correspond to the most abundant isotope peaks for each glycopeptide. The monoisotopic masses for all glycopeptides are listed in Table 1.