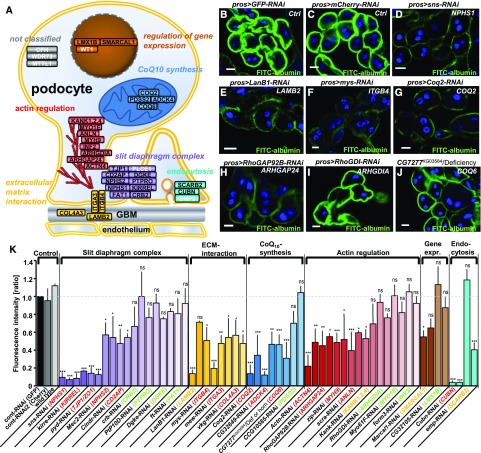
Figure 3.
Endocytosis assay in Drosophila GCN shows reduced uptake of FITC-albumin in the majority of orthologs of mammalian genes that if mutated cause nephrosis. (A) Known monogenic causes of SRNS in humans or mice are shown within their protein interaction complexes and subcellular localization in the podocyte. Cellular functions are classified as: slit diaphragm complex, ECM interaction proteins, actin regulators, regulators of gene expression, proteins that play a role in endocytosis, and CoQ10 synthesis genes. Gene names in white letters indicate that no ortholog was identified. (B–J) Shown are examples of GCN that were exposed to FITC-albumin for 30 seconds for a selection of genotypes. All scale bars represent 10 µm. The human ortholog is denoted in white. (B) Nephrocytes expressing control RNAis against mCherry (B) or GFP (C) exhibit strong FITC-albumin uptake whereas cells expressing an RNAi directed against the nephrin ortholog sns result only in minimal uptake (D). Reduced uptake is also observed upon knockdown of the orthologs of LAMB2 (E), ITGB4 (F), COQ2 (G), and ARHGAP24 (H). Knockdown of the ortholog of ARHGDIA on the other hand shows uptake similar to control levels (I). An allele of the ortholog of COQ6 hemizygous over a corresponding deficiency shows reduced uptake as well (J). (K) Quantitation of fluorescent intensity from FITC-albumin uptake is shown. The human ortholog is denoted in brackets. Genes are grouped into functional complexes denoted on top (compare with figure in A). The human ortholog is colored in red when the uptake was significantly reduced in two RNAis and in green when no significant difference to control (mCherry) was observed (P<0.05) for two RNAis. Genes where significant reduction of tracer uptake was observed with one RNAi but did not confirm in the only available second RNAi are denoted as undetermined (yellow). Wild type nephrocytes and GCN expressing an RNAi directed against mCherry showed uptake that is comparable to GFP-RNAi. Knocking down orthologs of genes involved in the slit diaphragm complex, ECM interaction, CoQ10 synthesis, and actin regulation resulted in impaired tracer uptake. The p element insertion allele of the ortholog of COQ6 is quantified homozygous and hemizygous over a short deficiency both resulting in reduced uptake. Values are presented as mean±SD of the ratio to a control experiment (GFP-RNAi) done in parallel, n=3–4 per genotype. Statistical significance was calculated using ANOVA and Dunnet post hoc analysis. ACTN4, actinin, α4; ADCK4, aarf domain-–containing kinase 4; ANLN, actin-binding protein anillin; ARHGAP24, rho gtpase–activating protein 24; ARHGDIA, rho gdp–dissociation inhibitor α; CD2AP, cd2-associated protein; COL4A3, collagen Type IV, α-3; COQ2, coq2 homolog (s. cerevisiae); COQ6, coq6 homolog (s. cerevisiae); CRB2, crumbs homolog 2 (drosophila); CUBN, cubilin; DGKE, diacylglycerol kinase, ε, 64-kd; FAT1, fat tumor suppressor homolog 1 (drosophila); INF2, inverted formin 2; ITGA3, integrin α-3; ITGB4, integrin β-4; KANK1, kn motif- and ankyrin repeat domain–containing protein 1; KANK2, kn motif– and ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 2; KANK4, kn motif– and ankyrin repeat domain–containing protein 4; KIRREL, kin of ire–like; LAMB2, laminin β-2; LMX1B, lim homeobox transcription factor 1 β; MYH9, myosin heavy chain 9, nonmuscle; MYO1E, myosin 1e; NPHS1, nephrin; NPHS2, podocin; PDSS2, prenyl diphosphate synthase, subunit 2; PTPRO, protein-tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type o; SCARB2, scavenger receptor class b, member 2; SMARCAL1, swi/snf-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a-like protein 1; TJP1, tight junction protein 1.