Abstract
Phosphate (Pi) limitation is a constraint for plant growth and development in many natural and agricultural ecosystems. In this study, a gene encoding Zea mays L. protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit A, designated ZmPP2AA1, was induced in roots by low Pi availability. The function of the ZmPP2AA1 gene in maize was analyzed using overexpression and RNA interference. ZmPP2AA1 modulated root gravitropism, negatively regulated primary root (PR) growth, and stimulated the development of lateral roots (LRs). A detailed characterization of the root system architecture (RSA) in response to different Pi concentrations with or without indole-3-acetic acid and 1-N-naphthylphthalamic acid revealed that auxin was involved in the RSA response to low Pi availability. Overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 enhanced tolerance to Pi starvation in transgenic maize in hydroponic and soil pot experiments. An increased dry weight (DW), root-to-shoot ratio, and total P content and concentration, along with a delayed and reduced accumulation of anthocyanin in overexpressing transgenic maize plants coincided with their highly branched root system and increased Pi uptake capability under low Pi conditions. Inflorescence development of the ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing line was less affected by low Pi stress, resulting in higher grain yield per plant under Pi deprivation. These data reveal the biological function of ZmPP2AA1, provide insights into a linkage between auxin and low Pi responses, and drive new strategies for the efficient utilization of Pi by maize.
Introduction
Phosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient for plants. It serves both as a component of cellular materials, such as nucleic acids, membranes, and ATP, and as a key component in the regulation of numerous enzymatic activities and metabolic processes [1]. Despite its abundance in natural soil, inorganic phosphate (Pi) is often limiting for plants due to its strong affinity for cations and its rapid conversion to organic forms that are not readily available for plant uptake. To prevent P starvation, modification of the morphology of the RSA is one adaptive mechanism to increase exploration activity to facilitate plant acquisition of more Pi from the soil [2–5]. In Arabidopsis, low Pi availability attenuates PR growth, facilitates LR initiation and development, and increases root hair generation [6, 7]. The response of the RSA to Pi availability can be distinct between the dicotyledon Arabidopsis and monocotyledon Zea mays because the RSA and cellular organization patterning of individual roots can differ significantly between the two species [8–10]. Variation also exists among Zea mays genotypes in terms of the effects of Pi starvation on the RSA [11–14].
The phytohormone auxin is believed to play a central role in root architecture modifications in response to Pi deprivation [2, 15–20]. The application of exogenous auxin inhibits PRs and promotes LRs in Arabidopsis, mimicking the alteration of the RSA induced by Pi deficiency [2, 21]. Nacry et al. [18] proposed that the effects of Pi on the RSA, such as the shortening of PRs, inhibition of LR primordium initiation, and the stimulation of initiated LR primordium activation, could be caused by the redistribution of auxin through changes in auxin transport rather than auxin synthesis.
Polar auxin transport (PAT) is mediated by auxin influx and efflux carrier proteins; their polar cellular localization determines the directional transport of auxin between cells. In plants, PIN-FORMED (PIN) proteins are auxin efflux carriers [22–29]. The polar intracellular localization of these proteins is determined by reversible phosphorylation in the central hydrophilic loop through the reciprocal regulation of PID kinase and PP2A [30–32].
PP2A is a major Ser/Thr protein phosphatase consisting of multiple subunits, including the catalytic C subunit, the scaffolding A subunit, and the regulatory B subunit. The PP2A catalytic (C) subunit binds to the A subunit to form a constant dimeric core, which can be associated with different members of the variable B subunit family to produce several species of holoenzymes with distinct properties and functions [33, 34]. In Arabidopsis, three genes encode A subunits: PP2AA1 encodes the A1 isoform (also known as RCN1), PP2AA2 encodes the A2 isoform, and PP2AA3 encodes the A3 isoform [35]. The biological functions of the AtPP2AA isoforms partially overlap, but RCN1 plays a cardinal role, while the functions of PP2AA2 and PP2AA3 are only unmasked when RCN1 is absent. Loss of AtPP2AAs function causes abnormities, such as root agravitropism, cotyledon defects and root meristem collapse throughout seedling development, as well as aberrations in embryo development. The rosette leaf growth, stem elongation, and reproductive development of adult phenotypes also require the functioning of the A subunits [32, 35–39].
The rcn1 mutant was identified in a screening process for a root-curling response in the presence of NPA [40, 41]. Roots of rcn1 seedlings exhibit elevated basipetal auxin transport and a significant delay in gravitropism [39, 42]. It is clear that the phenotypes observed in rcn1 roots are caused by reduced PP2A activity because wild-type (WT) seedlings treated with low doses of protein phosphatase inhibitors can phenocopy rcn1 [43]. To date, most advances in the study of PP2AAs have focused on the model plant Arabidopsis, and knowledge of these important protein phosphatases in monocot crops remains limited.
Pharmacological protein phosphatase inhibitor studies, the expression profiles of PP2A subunits under stress conditions, and the use of loss-of-function mutants or overexpression/silencing of specific PP2A subunit isoforms suggest that PP2As participate in biotic and abiotic stress signaling pathways [44]. Two PP2A catalytic subunit genes in rice (Oryza sativa) are differentially expressed in organs and respond to drought, salinity, and heat stresses [45]. Additionally, cold stress down-regulates the mRNA levels of LePP2Ac1, LePP2Ac2, and LePP2Ac3 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) leaves. Salt stress induces the expression of StPP2Ac1, StPP2Ac2a, StPP2Ac2b, and StPP2Ac3 in potato (Solanum tuberosum) leaves [46]. Water deficiency up-regulates the transcript levels of TaPP2Ac-1 in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings, and the overexpression of TaPP2Ac-1 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) enhances drought tolerance [47]. The expression of TaPP2AbB"-a is up-regulated by NaCl, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and cold and abscisic acid (ABA) stresses. Overexpression of TaPP2AbB"-a in Arabidopsis enhances lateral root development under NaCl and mannitol stresses [48]. PP2A has been shown to play a role in the chilling response in Arabidopsis in studies investigating two PP2A interactors: TAP46 and the AtCHIP E3 ubiquitin ligase [49, 50]. The Arabidopsis RCN1 gene acts as an integrator of stress signaling and is a positive transducer of the response to ionic (Na+, K+), osmotic (mannitol), and oxidative (hydrogen peroxide) stress [36].
Many features of the functional analysis of PP2As reveal that they are key components of stress signaling transduction pathways, but whether they would respond to Pi deficiency remains unanswered. Moreover, knowledge of the responses of the RSA to Pi starvation in economically important crops is still limited because most studies have been conducted using Arabidopsis as a model system.
In this study, we produced ZmPP2AA1 overexpression and RNAi (ZmPP2AA1 OE and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi) transgenic maize lines to discover the physiological functions of PP2A in the effects of Pi availability on the root system under different Pi regimens. The results showed that ZmPP2AA1 was responsive to Pi stress. Relative to WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi plants, ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing plants presented inhibited and curly PRs with agravitropic growth, as well as increased LR density and LR length, independent of the Pi status of the plant. During Pi deprivation, LR and axial root (AR) formation was promoted in ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing plants, which formed a highly branched root system that increased Pi acquisition under Pi deficiency. Overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 modified the free IAA content in AR root tips and the sensitivity to exogenous IAA or NPA, which indicated that the regulation of ZmPP2AA1 may be associated with auxin signaling. In addition, overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 in maize enhanced Pi deficit stress tolerance and increased yields under Pi deficiency.
Materials and methods
Cloning and sequence analysis of ZmPP2AA1
Amino acid alignment of three PP2AA1 proteins from maize (Zea mays L.): ZmPP2AA1 (GRMZM2G 164352; protein ID: Q32SG2), GRMZM2G102858, GRMZM2G122135, and three PP2AA proteins from Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) was performed using the CLUSTAL X 2.0 program [51] and GeneDoc 3.2 program [52]. The HEAT (huntingtin, elongation factor 3, A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A and TOR1) repeats were identified according to Perry and Kleckner [53]. The corresponding genomic sequences and structures were obtained using the EnsemblPlants browser (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html). A phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA5 (http://www.megasoftware.net/mega5/mega.html) [54] with three aligned ZmPP2AA protein sequences; two rice PP2AA protein sequences: Osl_30535, Os09g0249700; one barley PP2AA protein sequence: MLOC_2967; and two Brachypodium PP2AA protein sequences: BRADI4G08720 and BRADI4G08790. The neighbor-joining (NJ) method was employed in the phylogenetic tree construction.
Construction of ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing and RNAi construct vectors in plants
The ORF and fragment for the ZmPP2AA1 (GRMZM2G164352) overexpressing and RNAi vectors, respectively, were obtained by PCR using maize root cDNA from the inbred line Qi-319 as a template. The complete ZmPP2AA1 ORF with BamHⅠ restriction sites at the 5' and 3' ends was amplified using the ZmPP2AA1 OE primers (S1 Table), and the PCR product was inserted into the modified binary plant vector pCAMBIA3300-PUbi::MCS-Tnos-P35S::bar (pCUB). The pCUB contains a phosphinothricin acetyltranferase gene (bar) that confers resistance to the herbicide glufosinate ammonium.
For the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi construct, a 403-bp fragment of the ZmPP2AA1-encoding sequence was amplified using ZmPP2AA1-specific primers (S1 Table). The amplified ZmPP2AA1 fragment was inserted in the sense orientation with respect to SmaⅠ and SpeⅠ, and in the antisense orientation with respect to BamHⅠ and SacⅠ on both sides of the rice intron in vector pTCK303. Subsequently, the hairpin structure was inserted into the pCUB vector to construct the RNAi plant expression vector pCAMBIA3300-pUbi::zmpp2aa1-Tnos-P35S::bar. The RNAi vector also contained a bar gene. The resultant plasmids were then introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 using the freeze-thaw method.
Maize transformation and regeneration
Maize transformation and regeneration were performed as previously described by Li et al. [55]. The plant material was the maize (Zea mays L.) elite inbred line Qi-319. The transformed plantlets were screened by spraying the herbicide Finale (contains 245 mg/l of glufosinate ammonium, produced by Aventis) at the 3-leaf stage, and the surviving seedlings were chosen for PCR. The herbicide-resistant and PCR-positive plants (T0) were transplanted in the field and self-pollinated for three generations. Every generation of transgenic plants was verified by herbicide selection and PCR.
PCR analysis and Southern blotting
Genomic DNA from young maize leaves was extracted according to the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method [56]. Detection of the ZmPP2AA1 and bar genes was performed by PCR with ZmPP2AA1-specific and bar full-length primers, respectively (S1 Table). The PCR annealing temperatures were 52°C for the 621-bp ZmPP2AA1 gene fragment and 56°C for the 560-bp bar gene fragment (S2 Fig). The genomic DNA isolated from the PCR-positive T3 transgenic maize leaves was digested with KpnⅠ, and then Southern blotting was conducted using a digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled ZmPP2AA1-specific probe according to the DIG system manual (Roche).
RNA isolation and qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from plant samples using TRIzol reagent (TaKaRa). DNase-treated RNA was used as a template for cDNA synthesis using the RT reagent kit (TaKaRa) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR was performed using a LightCycler 480 (Roche) with the SYBR® RT-PCR kit (TaKaRa) in 10-μL reaction volumes for each sample amplified through 40 cycles. The gene-specific primers ZmPP2AA1 RT-F and ZmPP2AA1 RT-R were used to detect ZmPP2AA1 cDNA. The primers actin RT-F and actin RT-R (S1 Table) were designed to amplify the maize actin gene fragment as an internal control. The relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method [57]. Each experiment was repeated three times.
Hydroponic culture for the short-term experiment
The hydroponic culture and Pi deficiency treatments were established and maintained as described by Li et al. [58]. Seeds from Qi-319 and homozygous transgenic lines were surface-sterilized with 70% ethanol and 0.1% HgCl and washed with deionized water. They were then germinated on moist filter paper at 28°C in the dark for 3 d and transferred to a sufficient phosphate (SP, 1,000 μM KH2PO4) nutrient solution (2 mM Ca(NO3)2.4H2O, 1.25 mM NH4NO3, 0.1 mM KCl, 0.65 mM K2SO4, 0.65 mM MgSO4, 10 mM H3BO3, 0.5 mM (NH4)6Mo7O24, 1 mM MnSO4, 0.1 mM CuSO4.5H2O, 1 mM ZnSO4.7H2O, and 0.1 mM Fe-EDTA). At the 2-leaf stage (8 d old), the endosperms were carefully excised from all seedlings. After a recovery period of 2 d in the SP solution, half of the seedlings were transferred to the SP solution, and the remaining seedlings were grown in a low phosphate (LP, 5 μM KH2PO4) solution. Next, 1 mM KCl was added as a source of additional potassium to the LP treatment. The initial pH value of the nutrient solution was adjusted to 6.0±0.1. The nutrient solution was refreshed every 3 d. The plants grew under a 14-h light/10-h dark cycle at 32/25°C with 700 μmol m-2 s-1 photon flux density in a greenhouse with a relative humidity of approximately 65%. After treatment for 15 d, the plants were harvested to measure the biomass, morphological parameters, and total P content.
Hormone treatment
The LP and SP nutrient solutions were supplemented with either 3 μM IAA or 3 μM NPA and cultured for 15 d.
Long-term experiment
Seeds of the WT and transgenic plants were sown in cylindrical plastic pots containing loam, perlite, and roseite at a 2:1:1 ratio. After germination, the seedlings were irrigated with the LP (5 μM KH2PO4) nutrient solution every 2 d. At the 3-leaf stage, the plants were thinned to one plant per pot. When the plants reached the inflorescence stage, the anthesis-silking interval (ASI) was recorded, and only one ear was maintained on each maize plant. Mature ears were harvested to measure the ear length and kernel number per ear. After drying to a constant weight, the weight of the kernels was recorded to determine the yield.
Quantification of biomass and P content
Root and shoot samples were harvested and dried at 80°C in an oven to a constant weight for biomass determination. Quantification of the total P content was performed using the method described by Murphy and Riley [59]. Approximately 200 mg of dried shoot or root samples were flamed to ash and dissolved in 4 ml of concentrated H2SO4 on an electric stove. The dissolved solution was diluted 10 times, and 0.5 ml of the diluted solution was added to 4 ml of coloration solution containing 3 mol/L H2SO4, 2.5% NH4M0O4, and 10% ascorbic acid. The absorbance was read at 660 nm. The P concentrations were expressed as mg P/g tissue DW, and the P contents were calculated by multiplying the P concentration by the DW, providing a value of mg P per plant.
Estimation of Pi uptake kinetic parameters
The Pi uptake kinetics were assessed according to Drew and Saker [60]. The hydroponic-cultured maize seedlings were treated with SP (1,000 μM KH2PO4) and LP (5 μM KH2PO4) for 15 d, and all maize plants were transferred to the nutrient solution without P supplementation for 24 h. The P-depleted plants were transferred to the initial nutrient solution supplemented with 50 μM Pi. One milliliter of solution from each pot was collected at 30-minute intervals to measure the amount of Pi removed from the solution and to calculate the rate of Pi uptake. The Pi uptake kinetic parameters were estimated according to the method described by Claassen and Barber [61] using three replicates.
Measurement of morphological parameters
For the sake of simplicity, primary roots, seminal roots and crown roots are referred to as ARs in this study. The number of ARs and LRs was counted according to Li et al. [9]. The PR length was measured with a ruler, and other root lengths were measured using the grid-line intersection method presented by Li et al. [9]. The total absorption area and effective absorption area of the roots were measured using the methyl blue method [62].
Free IAA measurements
The IAA concentrations were measured in the 1.5-cm tips of the ARs of the WT and transgenic plants. The roots of plants at 15 d after treatment (DAT) to SP or LP were washed with deionized water five times for surface clearing. The root tips were excised and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Two hundred milligrams of the pooled samples were analyzed using UPLC-MS/MS, i.e., a UPLC system (ACQUITY UPLC, Waters, Shanghai, China) and a triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer as described by Fu et al. [63] on the plant hormone measurement platform at the Institute of Genetics and Development Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean values of at least three independent sets of experiments. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance between mean values was determined using one-way ANOVA with the SPSS 16.0 program. Different letters are used to indicate means that are significantly different at the 0.05 level.
Results
Cloning, sequence analysis, genomic organization and phylogenetic tree analysis of ZmPP2AA1
According to the mRNA sequence of the deduced Zea mays L. protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit A (Accession NO. AY940682), a 1765-bp fragment of the complete open reading frame (ORF) was produced by PCR from maize seedling root cDNA. This sequence was designated as ZmPP2AA1. The predicated protein of ZmPP2AA1 comprises 583 amino-acid residues with a calculated molecular weight of 65 kDa and a theoretical isoelectric point of 4.93. The predicted ZmPP2AA1 protein shows 83.8%, 88.9%, and 87.6% amino acid identity with AtPP2AA1 (RCN1), AtPP2AA2, and AtPP2AA3, respectively (S1 Fig). The ZmPP2AA1 genomic sequence spans 6.7 kb and contains 13 exons, of which 12 are coding exons. This profile is similar to those of AtPP2AAs (Fig 1B). ZmPP2AA1 is located on chromosome 6 according to the maize genomic sequence at http://www.maizesequence.org/index.html. Another two ZmPP2AA homologs have also been found in maize. The deduced amino acid sequence of ZmPP2AA1 shares approximately 93% similarity with GMZM2G102858 and approximately 91% similarity with GMZM2G122135 (S1 Fig). All ZmPP2AA proteins contain classical “HEAT” repeats with similarity to AtPP2AAs (Fig 1A). The phylogenetic tree indicates that the PP2AA proteins from the grass family formed a major clade, while three AtPP2AA proteins formed a group (Fig 1C).
Fig 1. Alignment of HEAT repeats of ZmPP2AAs with AtPP2AAs, genomic organization of ZmPP2AAs and AtPP2AAs, and phylogenetic relationship analysis of PP2AAs between maize, Arabidopsis, rice, barley and Brachypodium.
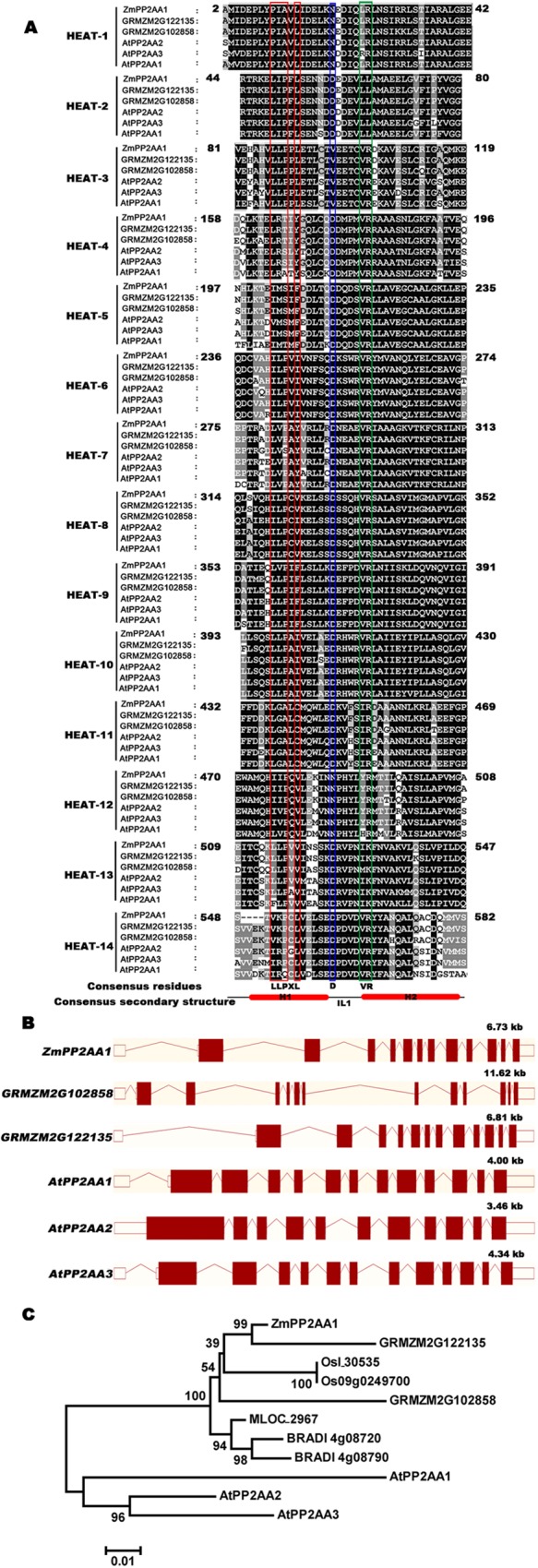
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of HEAT repeats in ZmPP2AAs with AtPP2AAs. The consensus “LLPXL” motifs in α-helix1 (H1) are boxed in red. The conserved Asp in the intra-loop (IL1) is boxed in blue. The consensus “VR” motifs in α-helix2 (H2) are boxed in green. Conserved residues between sequences are boxed in black or gray based on the degree of conservation. (B) Comparison of the genomic structures of ZmPP2AAs and AtPP2AAs. Exon/intron structures were obtained from the EnsemblPlants browser (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html). Red boxes and lines denote protein coding regions and introns, respectively. (C) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of PP2AAs. Bootstrap values are presented for all branches. Amino acid sequences for PP2AAs were obtained from http://www.uniprot.org: maize: ZmPP2AA1 (GRMZM2G164352), GRMZM2G102858, and GRMZM2G122135; rice: Osl_30535 and Os09g0249700; barley: MLOC_2967; Brachypodium: BRADI4G08720 and BRADI4G08790; Arabidopsis: AtPP2AA1 (AT1G25490), AtPP2AA2 (AT3G25800) and AtPP2AA3 (AT1G13320).
ZmPP2AA1 responds to Pi starvation
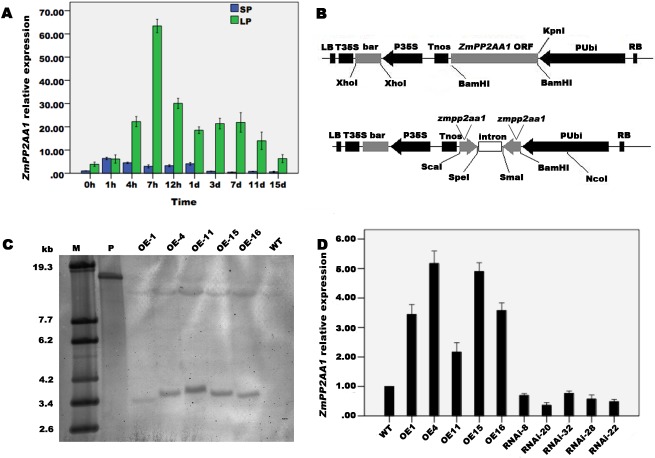
To assess the expression pattern of ZmPP2AA1 in response to Pi starvation, the relative transcript abundance of ZmPP2AA1 in the roots of the maize inbred line Qi-319 grown under Pi-deficient conditions was evaluated (Fig 2A). qRT-PCR revealed that the abundance of ZmPP2AA1 transcripts in roots treated with LP was increased relative to the SP treatment. During early Pi deprivation (1 h ~7 h after treatment), the transcripts continually increased and reached a peak after 7 h, followed by a remarkable decrease in the transcript abundance at 12 h; however, the expression of ZmPP2AA1 was maintained at a higher level after LP treatment compared with the SP treatment. The results indicate that ZmPP2AA1 is a gene that responds to Pi deficiency with induced expression.
Fig 2. Expression pattern of ZmPP2AA1 in roots and molecular characterization of ZmPP2AA1 transgenic maize plants.
(A) Expression pattern of ZmPP2AA1 in roots cultured in SP (1,000 μM KH2PO4) and LP (5 μM KH2PO4) nutrient solutions. The expression of ZmPP2AA1 was analyzed using qRT-PCR, and the value of the 0 h time point under the SP condition was considered 1-fold. (B) The T-DNA region of the vector used for the transformation. PUbi, a maize-constitutive ubiquitin promoter; bar, a biolaphos resistance phosphinothricin acetyl transferase gene; P35S, a promoter of CaMV35S from cauliflower mosaic virus. (C) Southern blotting analysis of the ZmPP2AA1 gene. M, λ-DNA/EcoT14Ⅰ molecular weight marker; P, vector plasmid; OE-1, OE-4, OE-11, OE-15, OE-16, T3 transgenic plants overexpressing ZmPP2AA1; WT, wild-type Qi-319. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of ZmPP2AA1 expression in the roots of maize transgenic lines and WT plants. The value of WT was considered 1-fold. Fold changes in the expression transcripts of all qRT-PCR analyses were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method with maize actin as an internal control. The data represent the average of three independent experiments ± SD.
Molecular characterization of ZmPP2AA1 transgenic maize plants
To quantify the effect of ZmPP2AA1 on plant responses to low Pi stress, we constructed transgenic plants with constitutive overexpression and RNA interference of ZmPP2AA1 (Fig 2B) and transformed the inbred line Q319. The transgenic plants (T0 to T2 generation) were screened with respect to resistance to the herbicide Finale (glufosinate) and by PCR (S2 Fig). The herbicide-resistant and PCR-positive independent transgenic lines were further identified using Southern blotting analysis. As shown in Fig 2C, an endogenous ZmPP2AA1 gene fragment was observed in all genotypes, while exogenous ZmPP2AA1 was presented as specific hybridization patterns. These results suggest that the exogenous fragments were stably integrated into the maize genome.
qRT-PCR was conducted to analyze the transcript abundance of ZmPP2AA1 in transgenic plants. Different expression levels were observed among different lines under normal conditions (Fig 2D). The overexpressing line OE-4 with a high transcription level (more than 5-fold higher than WT) and OE-11 with a low transcription level (2-fold higher than WT) among the overexpressing lines were chosen for further analysis. In RNAi plants, the presence of a few copies of ZmPP2AA1 transcripts suggested that the expression of ZmPP2AA1 was suppressed but not completely silenced. RNAi-20 with strong suppression (0.36-fold lower than WT) and RNAi-22 with mild suppression (0.48-fold lower than WT) were selected for subsequent characterization.
Overexpression and suppression of ZmPP2AA1 affect the development of the PR and LRs of maize
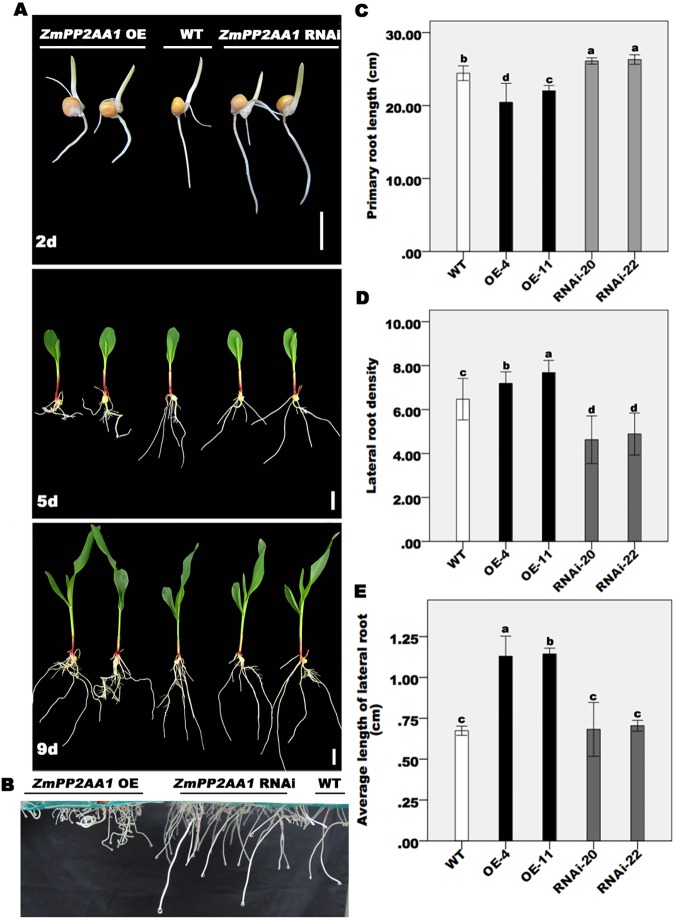
The Arabidopsis ROOTS CURL IN NAPHTHYLPHTHALAMIC ACID1 (RCN1) gene encodes the A1 isoform of the regulatory A subunit. The Arabidopsis mutant rcn1 was isolated based on the presence of curled roots in the presence of the auxin transport inhibitor NPA, and the roots of mutant seedlings presented an abnormal curling growth pattern without NPA. The mutation in RCN1 reduced the PR and hypocotyl elongation [41]. To determine whether the mutation in ZmPP2AA1 could affect maize root and hypocotyl growth patterns, the phenotypes of the WT, ZmPP2AA1 OE, and the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi line were characterized in hydroponic culture. Hypocotyl elongation of ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants displayed a normal pattern. The roots of the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants were curled, especially PR, which was not observed in the roots of the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi seedlings (Fig 3A and 3B; S2 Table). Compared with the WT, the PR length was reduced in the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants, while that in the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines was increased (Fig 3C; P< 0.05). The LR density and LR length of the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants were significantly increased compared with the WT plants, while there was a significant decrease in the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines (Fig 3D and 3E; P< 0.05). Together, the results suggest that ZmPP2AA1 regulates PR growth and the gravitropic response, and it alters LR architecture by stimulating formation and elongation.
Fig 3. Modification of the expression levels of ZmPP2AA1 in maize plants changes the root system architecture.
(A) Photographs are of representative WT, ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing and RNAi suppression transgenic seedlings grown in sufficient Pi (1,000 μM KH2PO4) nutrient solution for 2, 5 and 9 d after germination (DAG). (B) Root phenotype of the WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic seedlings at 6 DAG under normal conditions. (C, D, and E) The PR length, LR density (LR number/cm PR) and average LR length of 15 DAG WT, ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing plants and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi plants. Values are the means ± SD of each genotype. Different letters on the bars indicate significant differences between the means (P< 0.05).
ZmPP2AA1 is involved in root system architecture remodeling in response to Pi starvation
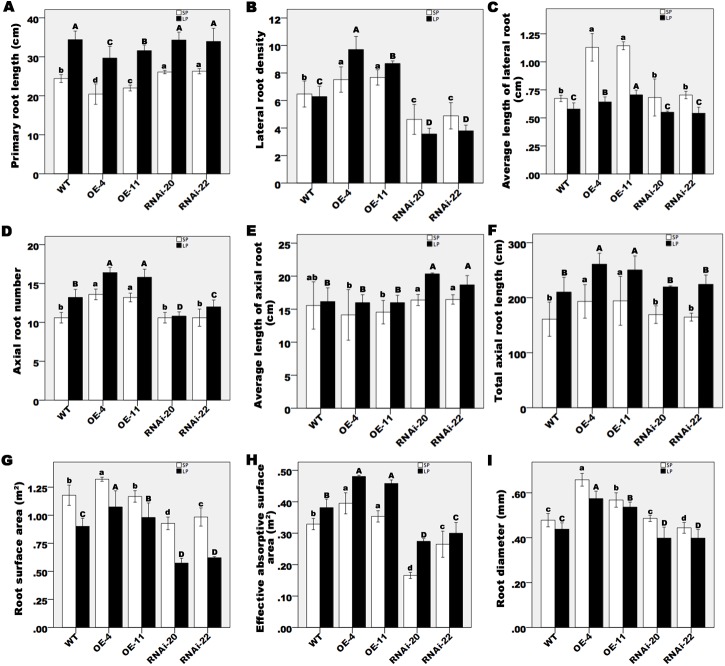
Modification of the RSA is a typical developmental response to Pi deficiency in the model eudicot Arabidopsis and in monocots such as rice and maize. An examination of the RSA response to Pi starvation in the variation of the expression level of ZmPP2AA1 demonstrated that the variation could affect the development of the maize root system. After being subjected to SP or LP conditions for 15 d, the hydroponically grown WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants were collected for root morphology analysis. The results showed that low Pi availability promoted PR and AR growth in all genotypes (Fig 4A, 4D, 4E and 4F). In addition, the average AR length in the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings was comparable to WT, and the higher number of ARs resulted in longer total AR lengths in the OE lines under the LP condition. The down-regulation of ZmPP2AA1 promoted AR elongation but had little effect on AR initiation. These results indicate that ZmPP2AA1 plays an important role in the AR development response to Pi deficiency.
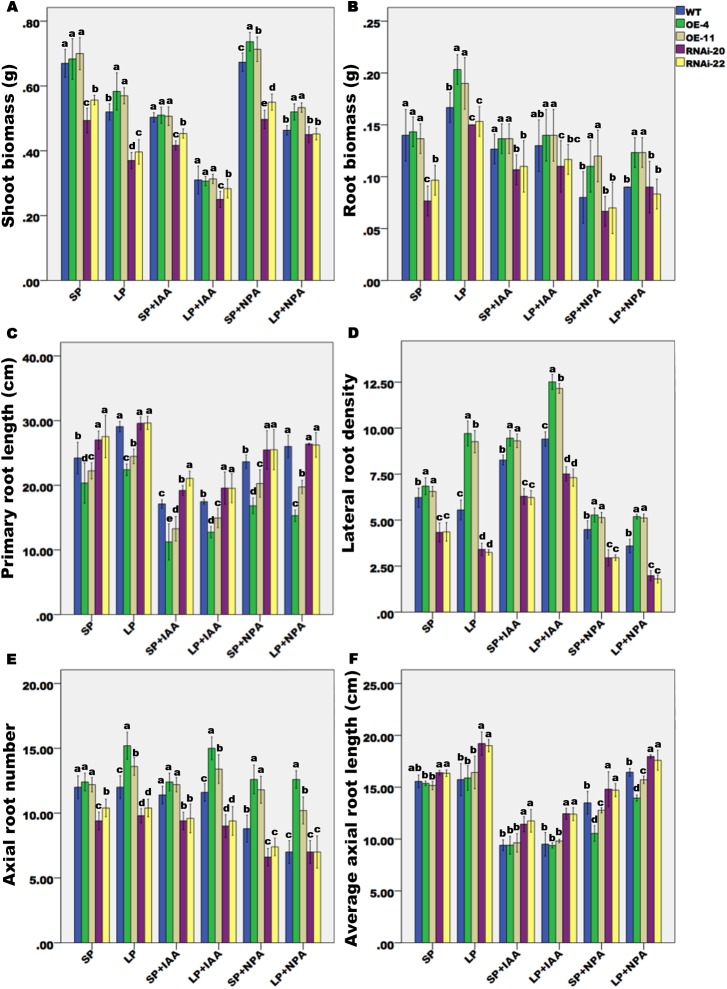
Fig 4. Root morphology of the WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants in response to SP or LP treatment for 15 d.
(A) PR length, (B) LR density (LR NO./cm PR), (C) average length of LR, (D) AR number, (E) average length of AR, (F) total length of AR, (G) root surface area, (H) effective absorptive surface area, and (I) root diameter of WT and transgenic plants hydroponically cultured under SP and LP conditions. Values are the means ± SD of each genotype. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between the means (P< 0.05) under the same conditions.
Modification of the expression of ZmPP2AA1 in maize also influenced LR development under the LP condition. LP inhibited LR elongation in all lines (Fig 4C). In the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines, the lateral root density was increased by LP stress, whereas a clear reduction was observed in the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines (Fig 4B). A robust root system of the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings was formed in comparison to the WT and RNAi lines (Fig 4I). Pi starvation significantly decreased the total root surface area, but the effective absorptive surface area increased in all lines (Fig 4G and 4H). In addition, compared with WT, the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings exhibited a larger effective absorptive surface area, whereas a smaller area was observed in the RNAi lines. These results indicate that overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 induced a highly branched root system with improved ARs and LRs in response to LP.
Overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 enhances tolerance to Pi deficiency in transgenic maize
After 11 d of Pi deficiency, the leaf veins and stems of the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi seedlings had accumulated anthocyanin, a typical Pi starvation response in plants [1], but the responses of the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines were delayed. Compared with the seedlings grown under SP conditions, the DWs of the shoots of all seedlings grown under LP conditions were reduced, whereas the root DWs increased (Table 1). These results indicate that Pi deficiency favored root growth over shoot growth, which resulted in an increased root-to-shoot ratio of Pi-deprived plants compared with Pi-sufficient plants (Table 1). Under SP conditions, ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing seedlings exhibited comparable root and shoot biomasses to the WT plants but an 18% higher root biomass and a 12% higher shoot biomass than the WT plants under LP conditions. These findings suggest that the overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 led to delayed anthocyanin accumulation and resulted in a much higher biomass under Pi starvation.
Table 1. Biomass of WT and transgenic plants under SP and LP conditions.
| Dry weight (g) | WT | OE-4 | OE-11 | RNAi-20 | RNAi-22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | ||||||
| SP | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | |
| LP | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 c | 0.16 ± 0.01 bc | |
| Shoot | ||||||
| SP | 0.67 ± 0.01 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 ab | 0.70 ± 0.01 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 c | 0.49 ± 0.02 c | |
| LP | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 0.58 ± 0.02 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 d | 0.40 ± 0.01 c | |
| Root/shoot | ||||||
| SP | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | |
| LP | 0.32 ± 0.01 c | 0.35 ± 0.02 b | 0.33 ± 0.02 bc | 0.41 ± 0.02 a | 0.40 ± 0.03 a | |
The DWs of the roots and shoots of the WT, overexpressing (OE-4 and OE-11), and RNAi (RNAi-20 and RNAi-22) plants were determined after drying to a constant weight in an oven at 80°C. Values presented are the means ± SD (n = 5). Values followed by different letters indicate significant differences (P< 0.05) among seedlings grown under the same Pi conditions.
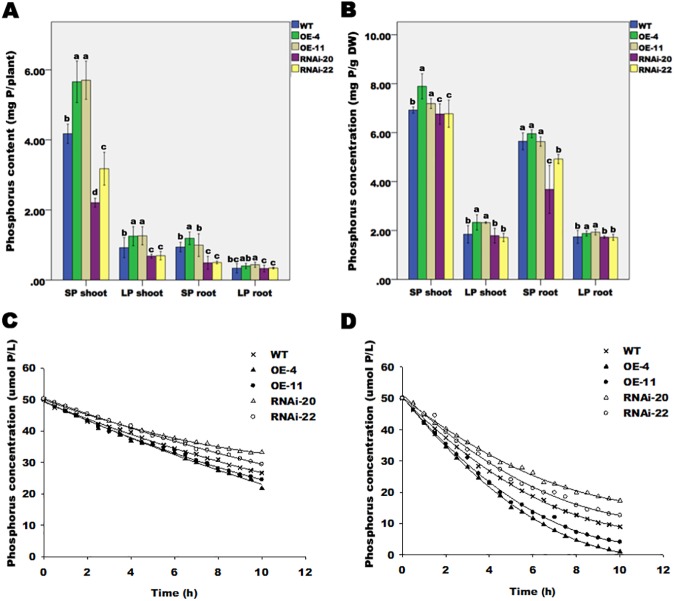
Total P accumulation increases in ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing transgenic maize plants during Pi deprivation
To address the effect of ZmPP2AA1 on Pi homeostasis, we measured the total P contents (mg P/plant) and P concentrations (mg P/g DW) in WT and transgenic plants grown under SP or LP treatment for 15 d (Fig 5A and 5B). Under SP conditions, OE-4 and OE-11 had 35% and 37% higher shoot P contents, respectively, than WT. In contrast, RNAi-20 and RNAi-22 had 47% and 24% lower shoot P contents, respectively, compared with WT. OE-4 had the highest root P content (1.19 mg P), while RNAi-20 had the lowest root P content (0.49 mg P). Under Pi-deficient conditions, the shoot and root P contents decreased in all plants. In comparison to WT, ZmPP2AA1 OE exhibited a 36% higher average shoot P content, whereas a reduction of 22% was observed in ZmPP2AA1 RNAi.
Fig 5. Enhanced Pi absorptive capacity enables ZmPP2AA1 OE to accumulate more phosphorus than the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi plants.
WT and transgenic plants were grown under SP or LP conditions for 15 d. Phosphorus content (A) and phosphorus concentration (B) in WT and transgenic plants. Values represent the means ± SD. Different letters above the bars are used to indicate significant differences (P< 0.05) among means under the same conditions. (C, D) Pi uptake kinetics in WT and transgenic plants under SP and LP conditions. The maize seedlings were subjected to SP (C) and LP (D) conditions for 15 d and were then transferred to Pi starvation conditions without P supplementation for 24 h. The P-depleted plants were transferred to the initial nutrient solution supplemented with 50 μM Pi for the depletion experiment. Pi uptake was measured as the Pi removed from the nutrient solution over time. The points represent observed values. The curve was fitted using an expression based on Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
We calculated the P concentration as the total P content normalized to the biomass (mg P/g DW) (Fig 5B). The down-regulation of ZmPP2AA1 significantly reduced (P<0.05) the shoot P concentrations compared with the WT and ZmPP2AA1 OE plants under both SP and LP conditions (Fig 5B). There were no significant differences (P> 0.05) in root P concentrations among the WT and overexpressing lines under SP conditions, but under LP conditions, the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings had significantly higher P concentrations (P< 0.05) in the shoots and roots compared with the WT. These results suggest that plants overexpressing ZmPP2AA1 with highly branched root systems have higher phosphate acquisition capability and accumulate more P in response to LP treatment. The maintenance of higher P concentrations could help alleviate plant growth retardation under Pi stress.
Different P uptake capacities of ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing and RNAi transgenic maize plants
To determine whether the variations among genotypes with respect to the total P contents and concentrations were driven by differences in P influx, we measured the P uptake kinetics. Examples of the results obtained for the plants subjected to SP and LP conditions in the depletion experiments are shown in Fig 5C and Fig 5D, respectively. The rate of depletion in plants grown in the SP solution (Fig 5C) was relatively gradual in comparison with plants grown in the LP solution (Fig 5D). ZmPP2AA1 OE displayed a steeper slope compared with the other plants, reflecting a higher rate of P uptake (Fig 5C and 5D). Table 2 shows the Pi uptake parameters for the WT and transgenic plants grown in the presence of different Pi levels. In comparison to the plants subjected to SP conditions, the Pi uptake capability of all plants subjected to LP conditions increased remarkably, as indicated by their increased maximal P uptake rate (Imax), lower Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) and lower minimal concentration (Cmin) (Table 2). Differences in Pi uptake parameters were also observed among the WT and transgenic plants. Regardless of Pi treatment, the Imax values of ZmPP2AA1 OE were higher whereas those of ZmPP2AA1 RNAi were lower than the WT. Compared with the WT, the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings exhibited significantly lower Km and Cmin parameters whereas the ZmPP2AA1 RNAi seedlings exhibited remarkably higher values (Table 2, P< 0.05) under LP conditions. These data indicate an enhanced rate of Pi uptake in the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants, which might explain the increased accumulation of total P in the overexpressing plants.
Table 2. Pi uptake kinetics in WT and transgenic plants under SP and LP conditions.
| WT | OE-4 | OE-11 | RNAi-20 | RNAi-22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imax (μmol l-1 h-1) | |||||
| SP | 2.80 ± 0.05 c | 3.31 ± 0.05 a | 3.15 ± 0.02 b | 2.55 ± 0.03 d | 2.54 ± 0.01 d |
| LP | 7.00 ± 0.02 c | 8.78 ± 0.03 a | 8.20 ± 0.12 b | 5.48 ± 0.02 e | 6.58 ± 0.07 d |
| Cmin (μmol l-1) | |||||
| SP | 12.08 ± 1.38 c | 12.11 ± 0.54 c | 12.83 ± 1.15 c | 29.81 ± 0.45 a | 23.62 ± 2.03 b |
| LP | 7.76 ± 1.02 c | 1.83 ± 0.14 e | 3.24 ± 0.44 d | 15.5 ± 0.35 a | 12.32 ± 1.03 b |
| Km (μmol l-1) | |||||
| SP | 21.41 ± 1.06 c | 21.52 ± 0.42 c | 21.97 ± 0.87 c | 34.89 ± 0.30 a | 29.82 ± 2.73 b |
| LP | 18.36 ± 0.69 c | 14.02 ± 0.08 d | 15.04 ± 0.31 d | 24.20 ± 0.39 a | 20.01 ± 1.13 b |
The maize seedlings were subjected to SP and LP conditions for 15 d and were then transferred to Pi starvation conditions without P supplementation for 24 h. The P-depleted plants were transferred to the initial nutrient solution supplemented with 50 μM Pi for the depletion experiment. The Pi parameters were estimated according to the method described by Claassen and Barber [61]. Imax, maximal P uptake rate; Cmin, minimal concentration below which no further net influx occurred; Km, Michaelis-Menten constant. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3). Values followed by different letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level among different genotypes under the same Pi concentrations. WT, wild-type; OE-4 and OE-11, overexpressing lines; RNAi-20 and RNAi-22, RNA interference lines.
ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing maize plants produce higher yields than WT and RNAi plants under Pi starvation conditions
We used cylindrical pots with a low Pi concentration to assess the influence of Pi deficiency on inflorescence and kernel development of the maize plants. Compared with the overexpressing lines, a significantly longer anthesis-silking interval (ASI) was observed in the WT and RNAi plants (Table 3, P< 0.05). More tassel branches were found on the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants compared with the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines (Table 3). The yields of the plants are shown in Table 3. Compared with the WT, the ear weights of OE-4 and OE-11 increased by 45% and 26%, respectively, due to their larger kernels (higher 100-grain weights) and higher number of kernels per ear.
Table 3. Agronomic traits of WT and transgenic plants under Pi-deficient conditions.
| WT | OE-4 | OE-11 | RNAi-20 | RNAi-22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of tassel branches | 5.67 ± 0.58 b | 7.67 ± 0.58 a | 7.00 ± 0.58 a | 5.00 ± 0.58 b | 5.33 ± 0.58 b |
| ASI (days) | 3.67 ± 0.58 a | 1.67 ± 0.58 b | 1.33 ± 0.58 b | 4.33 ± 0.58 a | 4.00 ± 1.00 a |
| Ear length (cm) | 9.87 ± 0.40 c | 14.23 ± 0.81 a | 12.87 ± 0.60 b | 8.63 ± 0.49 d | 8.87 ± 0.25 d |
| Ear weight (g) | 34.87 ± 1.70 c | 50.47 ± 1.11 a | 43.83 ± 1.63 b | 30.30 ± 1.01 d | 31.90 ± 0.70 d |
| Grain number per ear | 235.00 ± 3.61 c | 262.67 ± 5.51 a | 250.33 ± 4.16 b | 230.00 ± 4.58 c | 232.00 ± 3.46 c |
| 100-grain weight (g) | 13.09 ± 0.26 c | 17.35 ± 0.30 a | 15.65 ± 0.26 b | 11.36 ± 0.27 d | 11.72 ± 0.26 d |
Plants were grown in cylindrical pots with LP (5 μM KH2PO4) supplementation. At the flowering stage, the tassel branches and ASI were determined. After harvesting, the ear length and grain number per ear were recorded, and dried ears were weighed to determine the kernel yields. Values are the means ± SD (n = 5). Values followed by different letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level between the WT and transgenic lines under LP conditions. WT, wild-type; OE-4 and OE-11, overexpressing lines; RNAi-20 and RNAi-22, RNAi lines.
Free IAA contents in the PR of ZmPP2AA1 OE are higher than those in WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi under SP but not LP conditions
Auxin plays a key role in root development and mediates the Pi starvation effects on the RSA [2, 15, 16, 18–20]. To examine whether the curly and inhibited PRs of the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines and the promotion of AR elongation in the seedlings grown under LP conditions were affected by the variation in auxin accumulation in roots, we measured the free IAA contents in the apical 1.5 cm of the AR tips of seedlings grown under SP or LP conditions (Table 4). The root tips of the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings with short and curly ARs accumulated more free auxin than the other two maize seedling genotypes (Table 4). This indicated that the changes in AR development might be attributable to the variation in auxin levels. Pi-starved WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi seedlings exhibited comparable concentrations of free IAA to those measured in the Pi-sufficient seedlings. By contrast, the root tips of the ZmPP2AA1 OE line had lower auxin levels under LP conditions.
Table 4. Free IAA content of WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants under SP and LP conditions.
| pg free IAA mg-1 FW | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | ZmPP2AA1 OE | ZmPP2AA1 RNAi | |
| SP | 20.22 ± 1.34 b | 27.54 ± 2.16 a | 20.64 ± 2.02 b |
| LP | 18.26 ± 1.70 b | 21.38 ± 2.19 a | 19.58 ± 1.65 b |
Q319 (WT), ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing line OE-4 and RNA interference line RNAi-20 were grown in SP (1,000 μM KH2PO4) or LP (5 μM KH2PO4) nutrient solution for 15 d. The apical 1.5-cm-long root tips of all plants were excised, and the free IAA content was determined in 200-mg pooled samples. Values are the means of three independent experiments. Values followed by different letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level under the same conditions. FW, fresh weight.
ZmPP2AA1 regulates an auxin response or auxin transport that is linked to root architecture remodeling under Pi deficiency
To determine the relationship between LP signaling and auxin sensitivity or auxin transport in ZmPP2AA1 OE, we analyzed the effect of IAA and NPA on maize RSA under LP and SP conditions (S3 Fig; Fig 6). The concentrations of applied IAA and NPA (both 3 μM) were determined based on preliminary work conducted using plants cultivated under a wide range of IAA and NPA levels. Exogenous IAA amplified the detrimental effect of Pi starvation on shoot growth (S3 Fig). Compared with SP+IAA, the shoot biomass decreased by 40% in response to the LP+IAA treatments (Fig 6A). IAA treatment (3 μM) hindered PR elongation and resulted in a shortened but thickened AR (S3 Fig; Fig 6C and 6F). The reduction in length was more substantial under LP+IAA conditions, demonstrating that IAA treatment suppressed or attenuated the positive effects of Pi deprivation on PR and AR elongation, leading to comparable root biomasses in the SP+IAA and LP+IAA seedlings (Fig 6B). The effects of IAA on the roots were similar in the WT and transgenic seedlings under SP or LP conditions.
Fig 6. WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants grown under SP or LP conditions respond differently to IAA and NPA.
WT, overexpressing and RNAi plants were cultured under SP or LP conditions with or without IAA or NPA for 15 d. (A, B) Shoot and root biomasses of the WT and transgenic plants grown under SP or LP conditions with or without IAA or NPA for 15 d. (C) Primary root length, (D) LR density, (E) AR number, and (F) average AR length of WT and transgenic seedlings subjected to control conditions or treated with IAA or NPA. Values represent the means ± SD. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05) between the means under the same conditions.
NPA-treated seedlings exhibited suppressed root growth and a similar shoot biomass to the non-treated control (S3 Fig; Fig 6A and 6B). NPA treatment enhanced the agravitropic phenotype of the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines, while both the WT and RNAi lines displayed a weak response (S3 Fig). In the preliminary experiment, 1 μM NPA resulted in apparent curving of the roots of the ZmPP2AA1 OE seedlings, whereas a root agravitropic phenotype was observed in the WT plants exposed to up to 3 μM NPA. The stimulatory effect of LP on PR growth was eliminated by NPA treatment, and the detrimental effects were more drastic in ZmPP2AA1 OE (Fig 6C). These results suggest that the overexpressing lines were more sensitive to the effect of the auxin transport inhibitor NPA on embryonic PR development, and the RNAi lines were not susceptible.
After 15 d of NPA treatment, the average AR length was barely affected (Fig 6F), and the numbers of ARs in the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines were strikingly reduced compared with the NPA controls under SP or LP conditions. However, the overexpressing lines were less sensitive to the effect of NPA treatment on AR numbers (Fig 6E). NPA decreased the number of LRs in all genotypes, and the LP+NPA treatment had stronger inhibitory effects on the RNAi lines compared with the SP+NPA treatment (Fig 6D).
Discussion
In the present study, we found that ZmPP2AA1 participated in the regulation of maize root development and played important roles in the response of maize seedlings to low phosphate stress. ZmPP2AA1 negatively regulated PR elongation and was involved in root gravitropism and LR development. Overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 in maize plants resulted in a highly branched root system, maintained excellent shoot growth, increased Pi uptake and P content in roots, and increased grain yield under Pi deficit conditions. These results indicate that ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing maize plants had greater tolerance for low phosphate conditions than the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi maize plants.
A high level of root branching has been reported to favor phosphorus uptake under conditions of low Pi availability [3, 64]. Compared with the WT and RNAi lines, the ZmPP2AA1 OE plants showed enhanced AR and LR formation. An extensive root system with a larger absorptive area enhances exploitation in the upper layer of soil that contains Pi nutrient-rich regions (Fig 4). Efficient P uptake kinetics is another factor accounting for the high Pi uptake under low Pi supply (Fig 5C and 5D; Table 2). Higher Imax and lower Km and Cmin values indicated that the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines had efficient Pi uptake (Table 2), which was related to the higher Pi contents and concentrations (Fig 5A and 5B).
Auxin plays a key role in maize root development [65–72]. It has been suggested that PP2A activity is required for the normal regulation of auxin transport in Arabidopsis [39]. Several auxin-regulated characteristics, such as the PR gravitropic response, PR elongation, and LR development, were altered in the ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants (Fig 3A–3E). Excessive free IAA in the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines (Table 4) and the different responses of the WT and ZmPP2AA1 transgenic plants to IAA and NPA (Fig 6) suggest that the regulation of ZmPP2AA1 in root development may be associated with auxin signaling.
Interestingly, the inhibited and curly PR roots were characterized as a result of the overexpression of ZmPP2AA1 in maize (Fig 3), while the similar PR phenotype in Arabidopsis was caused by loss-of-function of RCN1 [41]. The ZmPP2AA1 proteins exhibited a high amino acid sequence identity with AtPP2AAs and high conservation in the “HEAT” repeats (Fig 1A). The discrepant effects of PP2AA on root curling between maize and Arabidopsis may be attributed to the following: different responses to growth conditions [41]; differences in the roots of the dicotyledon Arabidopsis and monocot maize [8,10]; or differences in auxin distribution and accumulation patterns [27,28]. The ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines showed a relative weak phenotype, which may have occurred because RNA interference did not silence but did suppress ZmPP2AA1. ZmPP2AAs share high similarity in their amino acid sequences and are conserved in “HEAT” repeats, suggesting that ZmPP2AA1, one member of the PP2AA gene family, might have some functional redundancy with other members.
Several reports have indicated that PP2A responds to Pi starvation. An investigation of the transcriptional response of maize roots to Pi starvation revealed that one gene encoding the PP2AB’ kappa subunit (ID: Zm.85150) was up-regulated by low Pi availability [73]. Our qRT-PCR results showed that ZmPP2AA1 was significantly up-regulated by low Pi availability (Fig 2A). The phosphoproteome profiles of maize ARs under LP stress also revealed that the catalytic subunit isoform 2 of PP2A displayed dynamic temporal patterns induced by low Pi availability [58]. This phenomenon suggests that the protein phosphatase ZmPP2AA1 is involved in a complex that plays a role in Pi starvation signal transduction following the perception of a low Pi signal.
Modified RSA in response to low Pi availability is often considered to be an adaptive response to maximize the Pi uptake capacity of plants in low Pi environments [2, 7, 15, 74–77]. A shortened PR is one of the characteristics of the altered the RSA induced by Pi starvation in Arabidopsis seedlings [6]. By contrast, in the present study, AR elongation was promoted in maize seedlings by Pi deficiency (Fig 4F), which is consistent with other reports [9, 58]. Pi deficiency inhibited LR elongation in all lines (Fig 4C). Low Pi availability increased LR density in the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines but reduced it in the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi plants (Fig 4B). IAA or NPA treatment altered the effects of LP on ARs and LRs (Fig 6D–6F), suggesting that auxin may play a role in the effect of LP-induced root modification. However, ZmPP2AA1 OE or ZmPP2AA1 RNAi scarcely showed differences with the WT in the response of roots to Pi deficiency or the hormone treatments, except for LR density. These findings suggest that other factors or genes co-participate in the RSA response to LP.
The ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing transgenic seedlings grown under Pi deficit conditions formed a highly branched root system, which enhanced the absorptive capability of Pi uptake. In addition, a significantly higher dry weight, root-to-shoot ratio, total P content and concentration, and delayed and reduced accumulation of anthocyanin was observed in these ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing transgenic seedlings compared with the WT and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi lines. The results suggest that the overall growth and development of the ZmPP2AA1 OE lines indicated less Pi starvation stress.
Conclusions
Based on the phenotypes of the transgenic plants overexpressing ZmPP2AA1 or those with RNAi interference and their non-transgenic controls, it is concluded that ZmPP2AA1 is a key player in PR growth and postembryonic root development. Auxin appears to be involved in the physiological processes underlying AR and LR development of maize under Pi deficiency. This research provides information on the low nutrient availability signal and auxin, as well as root development responses to LP conditions. The superior performance of plants with ZmPP2AA1 overexpression under low Pi stress supports the application of ZmPP2AA1 overexpression in the engineering of maize with improved tolerance to low phosphate conditions.
Supporting information
ZmPP2AA1 ORF primers were used for full ORF amplification of ZmPP2AA1 ORF; ZmPP2AA1 OE and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi primers were used for overexpression and RNAi vector construction, respectively; ZmPP2AA1 PCR and bar PCR primers were used for ZmPP2AA1 and bar detection in transgenic plants, respectively; ZmPP2AA1 qRT and actin qRT primers were used for qRT-PCR for ZmPP2AA1 and actin, respectively.
(PDF)
WT and transgenic seedlings were grown under SP or LP conditions for 6 days. Seedlings exhibiting root curling were counted. Values are the means ± SD (n = 20). The experiment was repeated five times.
(PDF)
Conserved residues between sequences are boxed in black or gray based on the degree of conservation. Arabidopsis: AtPP2AA1 (AT1G25490), AtPP2AA2 (AT3G25800) and AtPP2AA3 (AT1G13320); maize: ZmPP2AA1 (GRMZM2G164352), GRMZM2G102858, and GRMZM2G122135; rice: Osl_30535 and Os09g0249700; barley: MLOC_2967; Brachypodium: BRADI4G08720 and BRADI4G08790.
(PDF)
(A) PCR analysis of the ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing T3 transgenic plants. M, DNA marker DL2,000; +, the PCR product of plasmid pCAMBIA3300-PUbi::ZmPP2AA1-Tnos-P35S::bar; -, the PCR product of H2O as a negative control template; WT, untransformed control Qi-319; OE-1, OE-4, OE-11, OE-15, OE-16, different ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing transgenic lines. (B) PCR analysis of ZmPP2AA1 RNAi T3 transgenic plants for the bar gene. M, DNA marker DL2,000; +, the PCR product of plasmid pCAMBIA3300-PUbi::zmpp2aa1-Tnos-P35S::bar as a positive control; WT, untransformed control Qi-319; RNAi-8, RNAi-10, RNAi-20, RNAi-22, RNAi-28, RNAi-32, different ZmPP2AA1 RNAi transgenic lines.
(PDF)
Bar = 5 cm.
(PDF)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the expertise of Miss Shuang Fang and Dr Jinfang Chu (National Center for Plant Gene Research, Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China) in the determination of the IAA contents. We also thank American Journal Experts for their language polishing.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the National Genetically Modified Organism Major Projects of China (2011ZX08003-005) (http://program.most.gov.cn). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Marschner H. Functions of Mineral Nutrients: Macronutrients Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants (Second Edition). London: Academic Press; 1995. p. 229–312. [Google Scholar]
- 2.López-Bucio J, Hernández-Abreu E, Sánchez-Calderón L, Nieto-Jacobo MF, Simpson J, Herrera-Estrella L. Phosphate availability alters architecture and causes changes in hormone sensitivity in the Arabidopsis root system. Plant Physiol. 2002;129(1):244–56. doi: 10.1104/pp.010934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lynch JP, Brown KM. Root strategies for phosphorus acquisition: Springer Netherlands; 2008; 7: 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Niu YF, Chai RS, Jin GL, Wang H, Tang CX, Zhang YS. Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: a review. Ann Bot-london. 2013;112(2):391–408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Péret B, Clément M, Nussaume L, Desnos T. Root developmental adaptation to phosphate starvation: better safe than sorry. Trends Plant Sci. 2011;16(8):442–50. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.López-Bucio J, Cruz-RamíRez A, Herrera-Estrella L. The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003;6(3):280–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Williamson LC, Ribrioux SP, Fitter AH, Leyser HM. Phosphate availability regulates root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001;126(2):875–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hochholdinger F, Zimmermann R. Conserved and diverse mechanisms in root development. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008;11(1):70–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li Z, Gao Q, Liu Y, He C, Zhang X, Zhang J. Overexpression of transcription factor ZmPTF1 improves low phosphate tolerance of maize by regulating carbon metabolism and root growth. Planta. 2011;233(6):1129–43. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1368-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smith S, Smet ID. Root system architecture: insights from Arabidopsis and cereal crops. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367(367):1441–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bayuelo-Jiménez JS, Gallardo-Valdéz M, Pérez-Decelis VA, Magdaleno-Armas L, Ochoa I, Lynch JP. Genotypic variation for root traits of maize (Zea mays L.) from the Purhepecha Plateau under contrasting phosphorus availability. Fuel & Energy Abstracts. 2011;121(3):350–62. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP. Mapping of QTL controlling root hair length in maize (Zea mays L.) under phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil. 2005;270(1):299–310. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP. Topsoil foraging and phosphorus acquisition efficiency in maize (Zea mays). Funct Plant Biol. 2005;32(8):749–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhu J, Lynch JP. The contribution of lateral rooting to phosphorus acquisition efficiency in maize (Zea mays) seedlings. Funct Plant Biol. 2004;31(10):949–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Al-Ghazi Y, Muller B, Pinloche S, TRANBARGER TJ, Nacry P, Rossignol M, et al. Temporal responses of Arabidopsis root architecture to phosphate starvation: evidence for the involvement of auxin signalling. Plant Cell Environ. 2003;26(7):1053–66. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jain A, Poling MD, Karthikeyan AS, Blakeslee JJ, Peer WA, Titapiwatanakun B, et al. Differential effects of sucrose and auxin on localized phosphate deficiency-induced modulation of different traits of root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007;144(1):232–47. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.092130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Miura K, Lee J, Gong Q, Ma S, Jin JB, Yoo CY, et al. SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodeling involves the control of auxin accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2011;155(2):1000–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.165191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nacry P, Canivenc G, Muller B, Azmi A, Van Onckelen H, Rossignol M, et al. A role for auxin redistribution in the responses of the root system architecture to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005;138(4):2061–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.060061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pérez-Torres C-A, López-Bucio J, Cruz-Ramírez A, Ibarra-Laclette E, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M, et al. Phosphate availability alters lateral root development in Arabidopsis by modulating auxin sensitivity via a mechanism involving the TIR1 auxin receptor. Plant Cell. 2008;20(12):3258–72. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shen C, Wang S, Zhang S, Xu Y, Qian Q, Qi Y, et al. OsARF16, a transcription factor, is required for auxin and phosphate starvation response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2013;36(3):607–20. doi: 10.1111/pce.12001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.López-Bucio J, Hernández-Abreu E, Sánchez-Calderón L, Pérez-Torres A, Rampey RA, Bartel B, et al. An auxin transport independent pathway is involved in phosphate stress-induced root architectural alterations in Arabidopsis. Identification of BIG as a mediator of auxin in pericycle cell activation. Plant Physiol. 2005;137(2):681–91. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.049577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vieten A, Sauer M, Brewer PB, Friml J. Molecular and cellular aspects of auxin-transport-mediated development. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12(4):160–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Adamowski M, Friml J. PIN-dependent auxin transport: action, regulation, and evolution. Plant Cell. 2015;27(1):20–32. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.134874 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Balzan S, Johal GS, Carraro N. The role of auxin transporters in monocots development. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:393 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Carraro N, Forestan C, Canova S, Traas J, Varotto S. ZmPIN1a and ZmPIN1b encode two novel putative candidates for polar auxin transport and plant architecture determination of maize. Plant Physiol. 2006;142(1):254–64. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.080119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Forestan C, Farinati S, Varotto S. The maize PIN gene family of auxin transporters. Front Plant Sci. 2012;3(3):16–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Forestan C, Meda S, Varotto S. ZmPIN1-mediated auxin transport is related to cellular differentiation during maize embryogenesis and endosperm development. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(3):1373–90. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.150193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Forestan C, Varotto S. PIN1 auxin efflux carriers localization studies in Zea mays. Plant Signal Behav. 2010;5(4):436–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yue R, Tie S, Sun T, Zhang L, Yang Y, Qi J, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of ZmPIN, ZmPILS, ZmLAX and ZmABCB auxin transporter gene families in maize (Zea mays L.) under various abiotic stresses. Plos One. 2015;10(3):199–214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Friml J, Yang X, Michniewicz M, Weijers D, Quint A, Tietz O, et al. A PINOID-dependent binary switch in apical-basal PIN polar targeting directs auxin efflux. Science. 2004;306(5697):862–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1100618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huang F, Zago MK, Abas L, van Marion A, Galvan-Ampudia CS, Offringa R. Phosphorylation of conserved PIN motifs directs Arabidopsis PIN1 polarity and auxin transport. Plant Cell. 2010;22(4):1129–42. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Michniewicz M, Zago MK, Abas L, Weijers D, Schweighofer A, Meskiene I, et al. Antagonistic regulation of PIN phosphorylation by PP2A and PINOID directs auxin flux. Cell. 2007;130(6):1044–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cho US, Xu W. Crystal structure of a protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimeric holoenzyme. Nature. 2007;445(7123):53–7. doi: 10.1038/nature05351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Janssens V, Goris J. Protein phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signaling. Biochem J. 2001;353(3):417–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhou HW, Nussbaumer C, Chao Y, Delong A. Disparate roles for the regulatory A subunit isoforms in Arabidopsis protein phosphatase 2A. Plant Cell. 2004;16(3):709–22. doi: 10.1105/tpc.018994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blakeslee JJ, Zhou HW, Heath JT, Skottke KR, Barrios JA, Liu SY, et al. Specificity of RCN1-mediated protein phosphatase 2A regulation in meristem organization and stress response in roots. Plant Physiol. 2008;146(2):539–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kwak JM, Moon JH, Murata Y, Kuchitsu K, Leonhardt N, Delong A, et al. Disruption of a guard cell-expressed protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit, RCN1, confers abscisic acid insensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2002;14(11):2849–61. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003335 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Larsen PB, Cancel JD. Enhanced ethylene responsiveness in the Arabidopsis eer1 mutant results from a loss-of-function mutation in the protein phosphatase 2A A regulatory subunit, RCN1. Plant J. 2003;34(5):709–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rashotte AM, Delong A, Muday GK. Genetic and chemical reductions in protein phosphatase activity alter auxin transport, gravity response, and lateral root growth. Plant Cell. 2001;13(7):1683–97. doi: 10.1105/TPC.010158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Deruère J, Jackson K, Garbers C, Söll D, Delong A. The RCN1-encoded A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A increases phosphatase activity in vivo. Plant J. 1999;20(4):389–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Garbers C, Delong A, Deruere JP, Soll D. A mutation in protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit A affects auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Embo J. 1996;15(9):2115–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shin H, Guo Z, Blancaflor EB, Masson PH, Chen R. Complex regulation of Arabidopsis AGR1/PIN2-mediated root gravitropic response and basipetal auxin transport by cantharidin-sensitive protein phosphatases. Plant J. 2012;22(5):555–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sukumar P, Edwards KS, Rahman A, Delong A, Muday GK. PINOID kinase regulates root gravitropism through modulation of PIN2-dependent basipetal auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009;150(2):722–35. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.131607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.País SM, Téllez-Iñón MT, Capiati DA. Serine/threonine protein phosphatases type 2A and their roles in stress signaling. Plant Signal Behav. 2009;4(11):1013–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yu RMK, Zhou Y, Xu ZF, Chye ML, Kong RYC. Two genes encoding protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunits are differentially expressed in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 2003;51(3):295–311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.País SM, González MA, Téllez-Iñón MT, Capiati DA. Characterization of potato (Solanum tuberosum) and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) protein phosphatases type 2A catalytic subunits and their involvement in stress responses. Planta. 2009;230(1):13–25. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0923-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Xu C, Jing R, Mao X, Jia X, Chang X. A Wheat (Triticum aestivum) protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit gene provides enhanced drought tolerance in tobacco. Ann Bot-london. 2007;99(3):439–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liu D, Li A, Mao X, Jing R. Cloning and characterization of TaPP2AbB"-α, a member of the PP2A regulatory subunit in wheat. PloS one. 2014; 9(4):e94430 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Harris DM, Myrick TL, Rundle SJ. The Arabidopsis homolog of yeast TAP42 and mammalian alpha4 binds to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A and is induced by chilling. Plant Physiol. 1999;121(2):609–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Luo J, Shen G, Yan J, He C, Zhang H. AtCHIP functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of protein phosphatase 2A subunits and alters plant response to abscisic acid treatment. Plant J. 2006;46(46):649–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(21):2947–8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB, Deerfield DWI. genedoc: Analysis and Visualization of Genetic Variation. Embnew News. 1996;4(4):págs. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Perry J, Kleckner N. The ATRs, ATMs, and TORs are giant HEAT repeat proteins. Cell. 2003;112(2):151–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011; 28: 2731–2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li B, Wei A, Song C, Li N, Zhang J. Heterologous expression of the TsVP gene improves the drought resistance of maize. Plant Biotechnol J. 2008;6(2):146–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00301.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sambrook JF, Russell DW. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3-Volume Set) 2001.
- 57.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li K, Xu C, Fan W, Zhang H, Hou J, Yang A, et al. Phosphoproteome and proteome analyses reveal low-phosphate mediated plasticity of root developmental and metabolic regulation in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014;83:232–42. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.08.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Murphy J, Riley JP. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta. 1962;27(00):31–6. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Drew MC, Saker LR. Nutrient supply and the growth of the seminal root system in barley: iii. compensatory increases in growth of lateral roots, and in rates of phosphate uptake, in response to a localized supply of phosphate. J Exp Bot. 1978;29(2):2496–506. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Claassen N, Barber SA. A method for characterizing the relation between nutrient concentration and flux into roots of intact plants. Plant Physiol. 1974;54(4):564–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Onanuga AO, Jiang P-a, Adl S. Effect of Phytohormones, Phosphorus and Potassium on Cotton Varieties (Gossypium hirsutum) Root Growth and Root Activity Grown in Hydroponic Nutrient Solution. J Agr Sci. 2012;4(3):93–110. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fu J, Chu J, Sun X, Wang J, Yan C. Simple, rapid, and simultaneous assay of multiple carboxyl containing phytohormones in wounded tomatoes by UPLC-MS/MS using single SPE purification and isotope dilution. Anal Sci. 2012;28(11):1081–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Postma JA, Dathe A, Lynch JP. The Optimal Lateral Root Branching Density for Maize Depends on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Availability. Plant Physiology. 2014:166: 590–602. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.233916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Jansen L, Roberts I, De RR, Beeckman T. Phloem-associated auxin response maxima determine radial positioning of lateral roots in maize. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367(1595):1525–33. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Majer C, Xu C, Berendzen KW, Hochholdinger F. Molecular interactions of ROOTLESS CONCERNING CROWN AND SEMINAL ROOTS, a LOB domain protein regulating shoot-borne root initiation in maize (Zea mays L.). Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367(1595):1542–51. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Saleem M, Lamkemeyer T, Schützenmeister A, Madlung J, Sakai H, Piepho HP, et al. Specification of cortical parenchyma and stele of maize primary roots by asymmetric levels of auxin, cytokinin, and cytokinin-regulated proteins. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(152):4–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.von Behrens I, Komatsu M, Zhang Y, Berendzen KW, Niu X, Sakai H, et al. Rootless with undetectable meristem 1 encodes a monocot-specific AUX/IAA protein that controls embryonic seminal and post-embryonic lateral root initiation in maize. Plant J. 2011;66(2):341–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04495.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Woll K, Borsuk LA, Stransky H, Nettleton D, Schnable PS, Hochholdinger F. Isolation, characterization, and pericycle-specific transcriptome analyses of the novel maize lateral and seminal root initiation mutant rum1. Plant Physiol. 2005;139(3):1255–67. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.067330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Xu C, Tai H, Saleem M, Ludwig Y, Majer C, Berendzen KW, et al. Cooperative action of the paralogous maize lateral organ boundaries (LOB) domain proteins RTCS and RTCL in shoot-borne root formation. New Phytol. 2015;207(4):1123–33. doi: 10.1111/nph.13420 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zhang Y, Paschold A, Marcon C, Liu S, Tai H, Nestler J, et al. The Aux/IAA gene rum1 involved in seminal and lateral root formation controls vascular patterning in maize (Zea mays L.) primary roots. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(17):4919–30. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhang Y, Von BI, Zimmermann R, Ludwig Y, Hey S, Hochholdinger F. LATERAL ROOT PRIMORDIA 1 of maize acts as a transcriptional activator in auxin signalling downstream of the Aux/IAA gene rootless with undetectable meristem 1. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(13):3855 doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lin HJ, Gao J, Zhang ZM, Shen YO, Lan H, Liu L, et al. Transcriptional responses of maize seedling root to phosphorus starvation. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(9):5359–79. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2636-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bonser AM, Lynch J, Snapp S. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on growth angle of basal roots in Phaseolus vulgaris. New Phytol. 1996;132(2):281–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Drew MC. Comparison of the effects of a localized supply of phosphate, nitrate, ammonium and potassium on the growth of the seminal root system, and the shoot, in barley. New Phytol. 1975;75(3):479–90. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Johnson JF, Vance CP, Allan DL. Phosphorus deficiency in Lupinus albus. Altered lateral root development and enhanced expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1996;112(1):31–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Linkohr BI, Williamson LC, Fitter AH, Leyser HMO. Nitrate and phosphate availability and distribution have different effects on root system architecture of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002;29(6):751–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
ZmPP2AA1 ORF primers were used for full ORF amplification of ZmPP2AA1 ORF; ZmPP2AA1 OE and ZmPP2AA1 RNAi primers were used for overexpression and RNAi vector construction, respectively; ZmPP2AA1 PCR and bar PCR primers were used for ZmPP2AA1 and bar detection in transgenic plants, respectively; ZmPP2AA1 qRT and actin qRT primers were used for qRT-PCR for ZmPP2AA1 and actin, respectively.
(PDF)
WT and transgenic seedlings were grown under SP or LP conditions for 6 days. Seedlings exhibiting root curling were counted. Values are the means ± SD (n = 20). The experiment was repeated five times.
(PDF)
Conserved residues between sequences are boxed in black or gray based on the degree of conservation. Arabidopsis: AtPP2AA1 (AT1G25490), AtPP2AA2 (AT3G25800) and AtPP2AA3 (AT1G13320); maize: ZmPP2AA1 (GRMZM2G164352), GRMZM2G102858, and GRMZM2G122135; rice: Osl_30535 and Os09g0249700; barley: MLOC_2967; Brachypodium: BRADI4G08720 and BRADI4G08790.
(PDF)
(A) PCR analysis of the ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing T3 transgenic plants. M, DNA marker DL2,000; +, the PCR product of plasmid pCAMBIA3300-PUbi::ZmPP2AA1-Tnos-P35S::bar; -, the PCR product of H2O as a negative control template; WT, untransformed control Qi-319; OE-1, OE-4, OE-11, OE-15, OE-16, different ZmPP2AA1 overexpressing transgenic lines. (B) PCR analysis of ZmPP2AA1 RNAi T3 transgenic plants for the bar gene. M, DNA marker DL2,000; +, the PCR product of plasmid pCAMBIA3300-PUbi::zmpp2aa1-Tnos-P35S::bar as a positive control; WT, untransformed control Qi-319; RNAi-8, RNAi-10, RNAi-20, RNAi-22, RNAi-28, RNAi-32, different ZmPP2AA1 RNAi transgenic lines.
(PDF)
Bar = 5 cm.
(PDF)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.