Fig 2. PbA-induced impairment of cognition is prevented in the absence of IL-33/ST2 pathway.
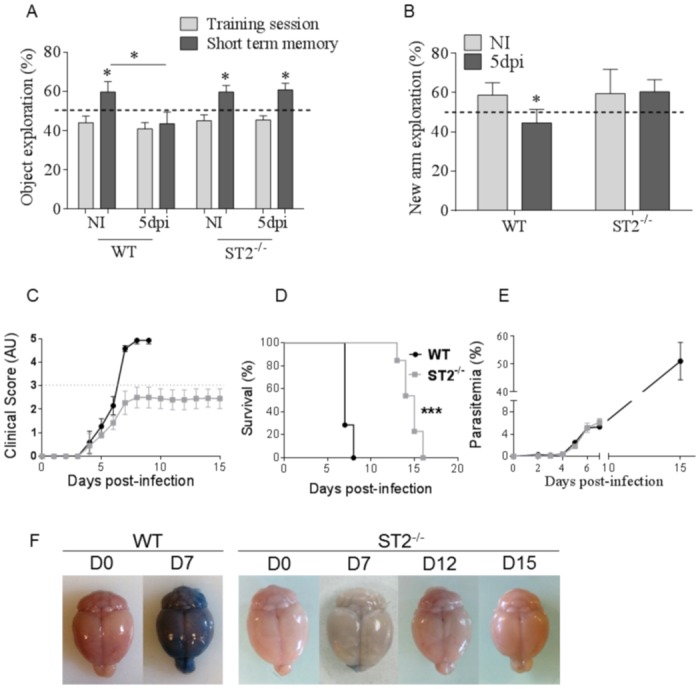
ST2-/- and WT mice were infected with 105 PbA-parasitized red blood cells. (A) Novel object recognition (NOR) investigated short term memory impairment 5 days post-infection (dpi). These results are representative of 2 independent experiments and shown as mean ± SEM with n = 9 to 12 mice per group. NOR was compared to the respective training session (*on the bar). (B) Y maze was used to assess hippocampal memory 5 dpi. These results are shown as mean ± SEM with n = 10 to 15 mice for WT and n = 9 to 10 for ST2-/- mice. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test (*p≤0.05). (C-E) Survival was followed (C), neurological signs were observed and translated into a clinical score, expressed in arbitrary units (AU) (D), and parasitemia was measured until day 7 (E). (F) Blood brain barrier leakage was assessed after Evan’s Blue injection on day 7 after PbA-infection in WT and ST2-/- mice (n = 4) and further on day 12 (n = 4) and 15 (n = 3) in surviving, ECM resistant ST2-/- mice. Kruskal-Wallis was applied, followed by Dunn’s comparison test (***p≤0.001).
