Figure 5.
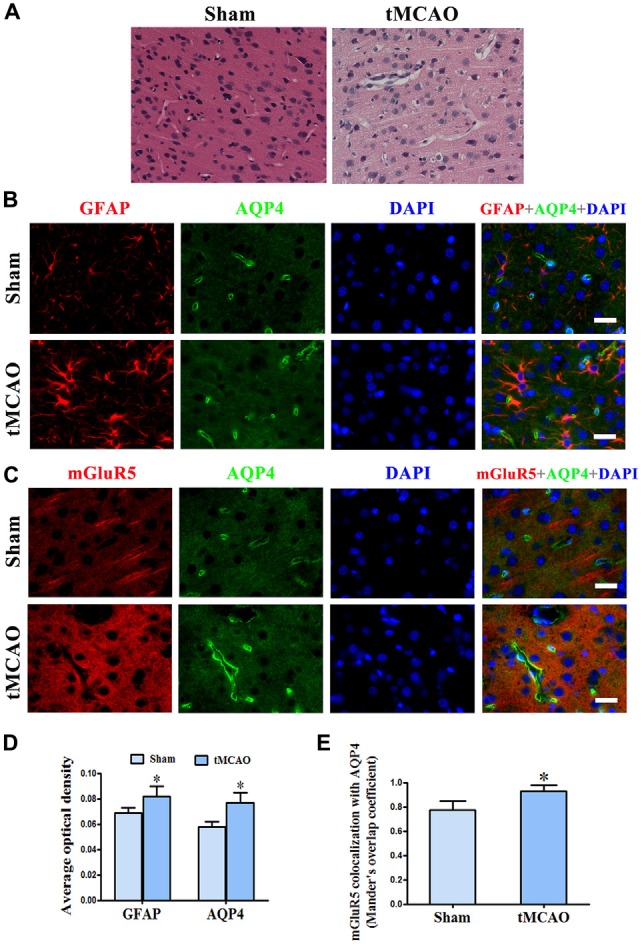
Increased co-expression of mGluR5 and AQP4 in a rat model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining showed that neuronal cells in the sham group were arranged regularly, and glial cells and capillary morphogenesis were normal. After tMCAO, most cell arrangement was disordered, with pyknotic or severely shrunken nuclei; in certain areas, hypervacuolization and cellular edema were found. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining showed the expression of GFAP (red) and AQP4 (green) in astrocytes, which increased after tMCAO. (C) Double immunofluorescence staining showed that mGluR5 (red) and AQP4 (green) were rarely co-expressed in pericapillary areas in the normal brain, but co-expression was increased in the pericapillary area and cell membranes of astrocytes after tMCAO. Scale bar shows 20 μm. (D) Statistical analysis of chart (B). (E) Colocalization of AQP4 and mGluR5 was determined using ImageJ software. Three independent fields containing more than three randomly selected images per condition in three different experiments were assessed and analyzed, and the average Mander’s overlap coefficient was calculated. *P < 0.05, compared to the sham group, graphed data show mean ± SD.
